This chapter considers an extended example, using Jini in a home audio situation. It uses many of the concepts of earlier chapters and shows how Jini can be used to build non-trivial systems
Traditional information systems concentrated on modelling information flows, and quite explicitly avoided physical systems. The advent of object-oriented systems changed this emphasis, with increased emphasis on the behaviour of real objects and how this could form the basis of an information system. In the meantime, there has been a huge amount of work in control systems, and increasing the computational power of everyday things such as dishwashers, washing machines and so on. One area in which the convergence of computer systems and devices has become a major commercial area is that of audio/visual systems. The change from analogue to digital sytems has opened up a large area, which goes far beyond copying MP3 files from one computer to another
The home A/V area is a battleground for ideologies and commercial interests. On the one hand are the set-top vendors, owning the cable systems that pump entertainment into many homes. Their vision is to widen their pipe, while still maintaining control. The professional audio and hifi community on the other hand, see the hifi system as control centre. And of course, the computer community sees the PC as centre of any home A/V system, due to its processing power, well-developed software systems, and the ability to handle digital signals without difficulty.
I belong to the PC-centric community to some extent - for even there, there are divergences of opinion. Most current A/V systems such as the Java Media Framework and the Microsoft Media Platform treat the A/V sources and sinks as though they are on the same machine, so that all processing is done locally. Agreed, JMF allows network access using HTTP or RTP, but it tries to hide the network layer and make all components appear to be local.
The mantra from Sun for many years is "the network is the computer." This could be applied to the A/V world: "the network is the A/V system." What makes it interesting for the A/V system is what a network can do: a wireless network can support friends visiting with their own A/V systems, joining in with yours to share music; it can support music following you around the house, switching from one set of speakers to another. This chapter is my attempt at building a network wireless audio system using Jini.
There have been many efforts to distribute A/V. Much of this is concerned with large servers, and these efforts have paid off with streaming media systems such as RealAudio. I want to look at a more local situation: my house is a medium size house, and now that I have a wireless network I can work in the lounge room, the family room, my study or even in one of the bedrooms. I like "music while you work" - either CDs, or the various community radio stations that I subscribe to, and possibly streaming audio from other stations in the world later. I don't have any children or partner there at the moment, but if I did, then they would have their own music sources and sinks and would share the house network. Friends might come and visit, with their own A/V sources and sinks and just join the house network. In a little while, guitars and microphones will have Bluetooth cards,so we will be able to have a local network band.
The wireless network density in my neighbourhood is low, but eventually I should be able to join a local community network, which should give me metropolitan access. I live in a city rich in music (Melbourne, Australia) and sometimes feel that I hardly need to go out because the local radio stations (RRR, PBS-FM) are so good, but soon I would also hope to tune into the folk concert on the other side of town through the community wireless network.
Okay: so how do we build middleware for an A/V network that is network-centric, rather than proprieter-centric? There has been one attempt that I know of to build a network-based A/V system, by Marco Lohse ("An open.middleware architecture for network-integrated multimedia"). This is CORBA-based, which gives it network objects. But a lot of their system has to be built on top of CORBA because it doesn't quite support what they want. Much of this extra structure seems to fall out quite easily under Jini.
I am approaching the rest of this chapter from a software-engineering viewpoint, trying to make a system as simple as possible for consumers (clients). If you have any comments on this, please let me know - after all, this is the system I using in my house right now, so if it can be made better, then I at least will be grateful!
There are many variables that affect how A/V is sourced, moved around a network and delivered
Interfaces should contain all the information about how to access services. With audio, all the information about a service can be quite complex: for example, a service might offer a CD track encoded in 16-bit stereo, big-endian, 44.1khz sampling in WAV format from an HTTP server. This information may be needed by a consumer that wants to play the file.
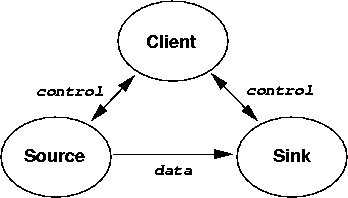
But in the type of A/V system I want to build there are three players:

For simplicity we define two interfaces: Source and Sink.
To avoid making implementation decisions about pull versus push, we
have methods to tell a source about a sink, a sink about a source, to tell
the source to play and the sink to record. Again, how they decide how to do this
is upto the source and sink. Sometimes this won't work: an HTTP source may not
be able to deliver to an RTP sink, or a WAV file may not be managed by an
MP3 player. If they don't succeed in negotiating tranport and content,
then an exception should be thrown. This violates the principle that a service
should be usable based on its interface alone, but considerably simplifies
matters for controller clients.
Notice that neither a source nor a sink have names or other descriptive information.
we choose to consider all this information as "additional service information" that
can be given by
A controller that wants to play a sequence of audio tracks to a sink will need
to know when one track is finished in order to start the next. The
play() and record() methods could block till
finished, or return immediately and post an event on completion.
The second method allows more flexibility, and so needs add/remove
listener methods for the events.
Finally, there are the exceptions that can be thrown by the methods.
Attempting to add a source that a sink cannot handle should throw
an exception such as IncompatableSourceException.
A sink that can handle only a small number of sources (for example, only
one) could throw an exception if too many sources are added. A source
that is already playing may not be able to satisfy a new request to play.
These considerations lead to a pair of high-level interfaces which seem to be suitable for controllers to manage sources and sinks:
/**
* Source.java
*/
package audio.common;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import net.jini.core.event.EventRegistration;
import net.jini.core.event.RemoteEventListener;
import java.rmi.MarshalledObject;
/**
* A source for A/V data
*/
public interface Source extends java.rmi.Remote {
int STOP = 1;
void play() throws
RemoteException,
AlreadyPlayingException;
void stop() throws
RemoteException,
NotPlayingException;
void addSink(Sink sink) throws
RemoteException,
TooManySinksException,
IncompatableSinkException;
void removeSink(Sink sink) throws
RemoteException,
NoSuchSinkException;
EventRegistration addSourceListener(RemoteEventListener listener,
MarshalledObject handback) throws
RemoteException;
}// Source
/**
* Sink.java
*/
package audio.common;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import net.jini.core.event.EventRegistration;
import net.jini.core.event.RemoteEventListener;
import java.rmi.MarshalledObject;
/**
* A sink for audio
*/
public interface Sink extends java.rmi.Remote {
int STOP = 1;
void record() throws
RemoteException,
AlreadyRecordingException;
void stop() throws
RemoteException,
NotRecordingException;
void addSource(Source src) throws
RemoteException,
TooManySourcesException,
IncompatableSourceException;
void removeSource(Source src) throws
RemoteException,
NoSuchSourceException;
EventRegistration addSinkListener(RemoteEventListener listener,
MarshalledObject handback) throws
RemoteException;
void removeSinkListener(RemoteEventListener listener) throws
RemoteException,
NoSuchListenerException;
}// Sink
The Java Media Framework (JMF) has methods such as getSupportedContentTypes()
which returns an array of strings. Other media toolkits have similar mechanisms.
This isn't type-safe: it relies on all parties having the same strings and attaching
the same meaning to each. In addition to this, if a new type comes along, there isn't
a reliable means of specifying this information to others. A type-safe system can at
least specify this by class files.
I have chosen to use interfaces instead of strings: a WAV interface,
an Ogg interface, etc. This doesn't easily allow extension
to the multiplicity of content type variations (bit size, sampling rate, etc),
but the current content handlers seem to be able to handle most of these
variations anyway, so it seems feasible to ignore them at an application
level.
The content interfaces are just place-holders:
package presentation;
public interface Ogg extends java.rmi.Remote {
}
Ogg interface. A sink that
can manage OggVorbis streams would also implement this interface.
In a similar way, I have chosen to represent the transport mechanisms by interfaces.
A transport sink will get the information from a source using some unspecified
network transport mechanism. The audio stream can be made available to any
other object by exposing an InputStream. This is a standard
Java stream, not the special one used by JMF. Similarly, a transport source
would make an output stream available for source-side objects to write data
into.
/**
* TransportSink.java
*/
package audio.transport;
import java.io.*;
public interface TransportSink {
public InputStream getInputStream();
}// TransportSink
/**
* TransportSource.java
*/
package audio.transport;
import java.io.*;
public interface TransportSource {
public OutputStream getOutputStream();
}// TransportSource
By separating the transport and content layers, we have a model that follows a part of the ISO 7-layer model: transport and presentation layers. The communication paths for a "pull" sink are
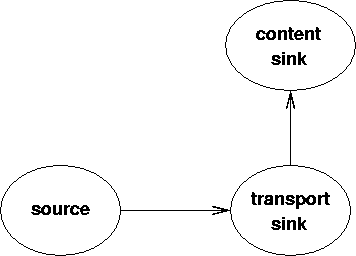
The classes involved in a "pull" sink could look like
An HTTP source makes an audio stream available as a document from an HTTP server.
All that it needs to tell a sink about is the URL for the document. There is a
little hiccup in this: a Java URL can be an http URL, or a
file URL, an ftp URL, etc. So I have defined a
class HttpURL to enforce that it is a URL accessible by the
HTTP protocol. The Java URL class is final, so we can't extend it and
have to wrap around it.
/**
* HttpURL.java
*/
package audio.transport;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class HttpURL implements java.io.Serializable {
private URL url;
public HttpURL(URL url) throws MalformedURLException {
this.url = url;
if (! url.getProtocol().equals("http")) {
throw new MalformedURLException("Not http URL");
}
}
public HttpURL(String spec) throws MalformedURLException {
url = new URL(spec);
if (! url.getProtocol().equals("http")) {
throw new MalformedURLException("Not http URL");
}
}
public URLConnection openConnection()
throws IOException {
return url.openConnection();
}
public InputStream openStream()
throws IOException {
return url.openStream();
}
}// HttpURL
The HttpSource interface just exposes an HttpURL:
/**
* HttpSource.java
*/
package audio.transport;
import audio.common.*;
import java.net.URL;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
public interface HttpSource extends Source {
HttpURL getHttpURL() throws RemoteException;
}// HttpSource
An HTTP source is a "pull" source: that is, a sink will fetch the data from it. A source of this type doesn't need to worry about listeners or playing the source data. All it needs to do is store the URL. An implementation of this could be
/**
* HttpSourceImpl.java
*/
package audio.http;
import audio.common.*;
import audio.transport.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.rmi.*;
import net.jini.core.event.EventRegistration;
import net.jini.core.event.RemoteEventListener;
import java.rmi.MarshalledObject;
/**
* Stores an HTTP reference
*/
public class HttpSourceImpl implements HttpSource, Remote {
private HttpURL url;
private HttpSourceImpl() {
}
public HttpSourceImpl(HttpURL url) {
this.url = url;
}
public HttpSourceImpl(URL url) throws MalformedURLException {
this.url = new HttpURL(url);
}
public HttpURL getHttpURL() {
return url;
}
public void play() {}
public void stop() {}
public void addSink(Sink sink) throws IncompatableSinkException { }
public void removeSink(Sink sink) {}
public EventRegistration addSourceListener(RemoteEventListener listener,
MarshalledObject handback) {
return null;
}
}// HttpSourceImpl
If the document is an OggVorbis document, then the service signals this by
implementing the Ogg interface
/**
* HttpOggSourceImpl.java
*/
package audio.http;
import audio.presentation.Ogg;
import audio.transport.HttpURL;
import java.net.*;
/**
* Adds Ogg interface to HttpSourceImpl for Ogg files
*/
public class HttpOggSourceImpl extends HttpSourceImpl
implements Ogg{
public HttpOggSourceImpl(HttpURL url) throws MalformedURLException {
super(url);
}
public HttpOggSourceImpl(URL url) throws MalformedURLException {
super(url);
}
}// HttpOggSourceImpl
An HTTP sink needs to find the URL from an HttpSource, open
a connection to it and get an InputStream.
The Java URL class makes this quite straightforward:
/**
* HttpSinkImpl.java
*/
package audio.transport;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class HttpSinkImpl implements TransportSink {
protected HttpSource source;
public HttpSinkImpl(HttpSource source) {
this.source = source;
}
public InputStream getInputStream() {
try {
HttpURL url = source.getHttpURL();
URLConnection connect = url.openConnection();
connect.setDoInput(true);
connect.setDoOutput(false);
InputStream in = connect.getInputStream();
return in;
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Getting in stream " + e.toString());
return null;
}
}
}// HttpSinkImpl
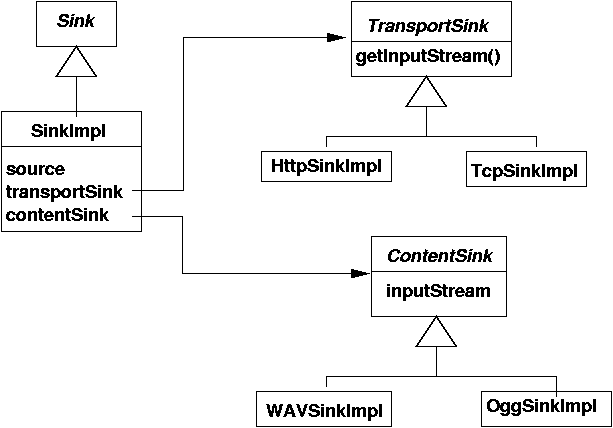
A ContentSink will get an InputStream from a
TransportSink. Then it can read bytes from this stream and
interpret it based on the content type it understands. There are some
content handlers in the Java JMF. But many are missing: MP3 files are encumbered
by patent rights, and encoders and decoders should cost (someone!) money to use,
so currently there is no MP3 player in JMF (well, there is an MPEG movie
player which can be called with no video stream...). There is very little activity
from Sun on new codecs, and there is no current OggVorbis player. There are attempts
to fill the gaps: for example, there is a pure Java Ogg Vorbis decoder, JOrbis,
and an MP3 decoder for JMF, JFFMPEG. But the situation has not settled down to
any clarity yet.
Im the meantime, it is easier to make O/S system
calls into players such as mpg123 or sox (under Unix). I have
generically labelled these as playmp3, etc, and these read
from a pipeline. I am being lazy here: I should have a createSink() should act like a proper factory and return the right
kind of content sink.
/**
* ContentSink.java
*/
package audio.pull;
import java.io.*;
import audio.presentation.*;
import audio.common.*;
public class ContentSink {
private InputStream in;
private OutputStream out;
private String cmd;
private boolean stopped = false;
private SinkImpl sink;
public static ContentSink createSink(SinkImpl sink,
InputStream in, Source source) {
String cmd = "";
if (source instanceof WAV) {
cmd = "playwav";
} else if (source instanceof Ogg) {
cmd = "playogg";
} else if (source instanceof MP3) {
cmd = "playmp3";
} else {
cmd = "true";
}
ContentSink csink = new ContentSink(sink, in, cmd);
return csink;
}
/**
* There should really be a
* WAVContentSink, OggContentSink, etc
* I cheated since they would be so simple
*/
private ContentSink(SinkImpl sink, InputStream in, String cmd) {
this.sink = sink;
this.in = in;
this.cmd = cmd;
}
public void record() {
Process proc = null;
InputStream err = null;
InputStream inn = null;
try {
proc = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
out = proc.getOutputStream();
err = proc.getErrorStream();
inn = proc.getInputStream();
} catch(IOException e) {
System.err.println("Playing " + e.toString());
// ignore
return;
}
int ch;
try {
while (((ch = in.read()) != -1) &&
(! stopped)) {
out.write(ch);
// System.out.println("Wrote byte");
}
} catch(IOException e) {
// ignore
System.err.println("Exception writing: " + e.toString());
int navail = 0;
try {
if ((navail = err.available()) > 0 ) {
byte avail[] = new byte[navail];
int nread = err.read(avail, 0, navail);
System.out.println("Error channel: " +
new String(avail));
}
if ((navail = inn.available()) > 0 ) {
byte avail[] = new byte[navail];
int nread = inn.read(avail, 0, navail);
System.out.println("Out channel: " +
new String(avail));
}
} catch(IOException ee) {
ee.printStackTrace();
}
return;
} finally {
if (stopped) {
System.out.println("Record stop called");
} else {
System.out.println("Record finished naturally");
stopped = true;
}
try {
if (proc != null) {
proc.destroy();
try {
// wait for soundcard to be released
proc.waitFor();
} catch(InterruptedException ei) {
System.out.println("Int " + ei);
}
}
in.close();
out.close();
} catch(IOException e) {
// ignore
System.out.println("Finally " + e);
}
sink.contentStopped();
}
}
public void stop() {
if (stopped) {
return;
}
stopped = true;
}
} // ContentSink
The playogg script for my Linux system is
#!/bin/sh
if [ $# -eq 0 ]
then
infile="-"
else
infile="$1"
fi
play -t ogg -c 2 $infile
wait # ensure /dev/dsp is free
sleep 3 # and give it extra time to be really free :-(
playmp3 is
#!/bin/sh
if [ $# -eq 0 ]
then
infile="-"
else
infile="$1"
fi
mpg123 -s $infile | sox -t raw -r 44100 -s -w -c 2 - -t ossdsp -w -s /dev/dsp
wait # ensure that /dev/dsp is given up
sleep 2 # and then give it more time, since "wait" isn't enough
artsd daemon is
running in the KDE enviroment. I typically kill it off, although there must be a
"better" way.)
A sink must create the appropriate transport and content handlers, and link the two together. It needs to look after listeners, and post events to them when they occur. This sink will handle a TCP and HTTP connections, and will manage WAV, Ogg and MP3 content.
/**
* SinkImpl.java
*/
package audio.pull;
import audio.transport.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.rmi.*;
import net.jini.core.event.EventRegistration;
import net.jini.core.event.RemoteEvent;
import java.util.Vector;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import net.jini.core.event.RemoteEventListener;
import net.jini.core.event.UnknownEventException;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import audio.common.*;
public class SinkImpl implements Sink, Remote {
private Source source;
private boolean stopped;
private CopyIO copyIO;
private Hashtable listeners = new Hashtable();
private int seqNum = 0;
private Remote proxy;
private MimeType contentType = null;
private InputStream in = null;
public SinkImpl() {
}
public void setProxy(Remote proxy) {
this.proxy = proxy;
}
public void record() throws RemoteException, AlreadyRecordingException {
if ((copyIO != null) && ( ! stopped)) {
throw new AlreadyRecordingException();
}
if (source == null) {
return;
}
stopped = false;
if (in == null) {
System.out.println("Couldn't get input stream");
stopped = true;
return;
}
// hand play over to a CopyIO object
// This will run a ContentSink in its own thread
copyIO = new CopyIO(this, in, source);
copyIO.start();
System.out.println("Play returning");
}
public void stop() throws RemoteException {
stopped = true;
if (copyIO != null) {
copyIO.stopRecord();
}
}
public void contentStopped() {
copyIO = null;
fireNotify(Sink.STOP);
System.out.println("Stopped");
}
public void addSource(Source source) throws
IncompatableSourceException,
TooManySourcesException {
TransportSink transportSink = null;
this.source = source;
// which transport sink to use?
if (source instanceof HttpSource) {
transportSink = new HttpSinkImpl((HttpSource) source);
in = transportSink.getInputStream();
} else if (source instanceof TcpSource) {
System.out.println("Setting up Tcp sink");
transportSink = new TcpSinkImpl((TcpSource) source);
in = transportSink.getInputStream();
System.out.println("Got tcp source input stream " + in);
} else {
throw new IncompatableSourceException();
}
}
public void removeSource(Source source) throws
RemoteException,
NoSuchSourceException {
if (this.source == source) {
this.source = null;
} else {
throw new NoSuchSourceException();
}
}
public EventRegistration addSinkListener(RemoteEventListener listener,
MarshalledObject handback) {
System.out.println("Adding listener: " + listener);
listeners.put(listener, handback);
System.out.println(" listeners size " + listeners.size());
return new EventRegistration(0L, proxy, null, 0L);
}
public void removeSinkListener(RemoteEventListener listener) {
listeners.remove(listener);
}
public void fireNotify(int evtType) {
Enumeration elmts = listeners.keys();
seqNum++;
System.out.println("Fire notify event seq id " + seqNum);
while (elmts.hasMoreElements()) {
RemoteEventListener listener = (RemoteEventListener) elmts.nextElement();
MarshalledObject handback = (MarshalledObject) listeners.get(listener);
RemoteEvent evt = new RemoteEvent(proxy, evtType, seqNum, handback);
System.out.println("Notifying listener " + listener);
try {
listener.notify(evt);
} catch(UnknownEventException e) {
// ??
} catch(RemoteException e) {
// ?
}
}
}
class CopyIO extends Thread {
private SinkImpl sink;
private ContentSink contentSink;
CopyIO(SinkImpl sink, InputStream in, Source source) {
contentSink = ContentSink.createSink(sink, in, source);
this.sink = sink;
}
public void stopRecord() {
if (contentSink != null) {
contentSink.stop();
}
}
public void run() {
contentSink.record();
}
}
}// SinkImpl
Each source will need a server to create, advertise it and keep it alive. So will each sink.
A sink server is
package audio.pull;
import net.jini.lookup.JoinManager;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceID;
import net.jini.discovery.LookupDiscovery;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceRegistrar;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import net.jini.lookup.ServiceIDListener;
import net.jini.lease.LeaseRenewalManager;
import net.jini.discovery.LookupDiscoveryManager;
import net.jini.discovery.DiscoveryEvent;
import net.jini.discovery.DiscoveryListener;
import java.rmi.RMISecurityManager;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import net.jini.config.*;
import net.jini.export.*;
import net.jini.id.UuidFactory;
import net.jini.id.Uuid;
import net.jini.core.entry.Entry;
import net.jini.lookup.entry.*;
import java.io.*;
/**
* PullSinkServer.java
*/
public class SinkServer {
// explicit proxy for Jini 2.0
protected Remote proxy;
protected SinkImpl impl;
private String sinkName = "No name";
private ServiceID serviceID;
public static void main(String argv[]) {
new SinkServer(argv);
// stay around forever
Object keepAlive = new Object();
synchronized(keepAlive) {
try {
keepAlive.wait();
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
// do nothing
}
}
}
public SinkServer(String[] argv) {
File serviceIDFile = null;
try {
impl = new SinkImpl();
} catch(Exception e) {
System.err.println("New impl: " + e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
String[] configArgs = new String[] {argv[0]};
try {
// get the configuration (by default a FileConfiguration)
Configuration config = ConfigurationProvider.getInstance(configArgs);
// and use this to construct an exporter
Exporter exporter = (Exporter) config.getEntry( "HttpSinkServer",
"exporter",
Exporter.class);
// export an object of this class
proxy = exporter.export(impl);
impl.setProxy(proxy);
sinkName = (String) config.getEntry( "HttpSinkServer",
"sinkName",
String.class);
serviceIDFile = (File) config.getEntry("HttpSinkServer",
"serviceIdFile",
File.class);
getOrMakeServiceID(serviceIDFile);
} catch(Exception e) {
System.err.println(e.toString());
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
// install suitable security manager
System.setSecurityManager(new RMISecurityManager());
JoinManager joinMgr = null;
try {
LookupDiscoveryManager mgr =
new LookupDiscoveryManager(LookupDiscovery.ALL_GROUPS,
null, // unicast locators
null); // DiscoveryListener
joinMgr = new JoinManager(proxy, // service proxy
new Entry[] {new Name(sinkName)}, // attr sets
serviceID, // ServiceID
mgr, // DiscoveryManager
new LeaseRenewalManager());
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
private void getOrMakeServiceID(File serviceIDFile) {
try {
ObjectInputStream ois =
new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(serviceIDFile));
serviceID = (ServiceID) ois.readObject();
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("Couldn't get service IDs - generating new ones");
try {
ObjectOutputStream oos =
new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(serviceIDFile));
Uuid uuid = UuidFactory.generate();
serviceID = new ServiceID(uuid.getMostSignificantBits(),
uuid.getLeastSignificantBits());
oos.writeObject(serviceID);
} catch(Exception e2) {
System.out.println("Couldn't save ids");
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
} // SinkServer
import net.jini.jeri.BasicILFactory;
import net.jini.jeri.BasicJeriExporter;
import net.jini.jeri.tcp.TcpServerEndpoint;
import java.io.File;
HttpSinkServer {
exporter = new BasicJeriExporter(TcpServerEndpoint.getInstance(0),
new BasicILFactory());
sinkName = new String("Jan's laptop");
serviceIdFile = new File("sinkServiceId.id");
}
This sink server depends on the following classes
audio.pull.SinkServer
audio.pull.SinkImpl
audio.pull.SinkImpl$CopyIO (an inner class)
audio.transport.HttpSinkImpl
audio.transport.TcpSinkImpl
audio.pull.ContentSink
audio.transport.TransportSink
All the classes in the audio.common package
java -classpath audio.pull.SinkServer.jar audio.pull.SinkServer http_sink_server.config
An individual piece of music may be a song, a movement from a classical symphony, an instrumental piece, and so on. Individual pieces of music may be collected together in many ways: a symphony is formed of movements; a pop CD is made up of individual songs; a CD may be made up from a collection of CDs; a boxed set of CDs will be made up of CDs themselves; the complete oeuvres of a composer is another classification. How do we want to represent all of these possibilities as services?
Databases of CDs such as CDDB have a simplistic solution: a CD is classified by an
Artist/Title. So CD is a collection of pieces, with no other structure.
This breaks down with "best of" collections and almost all classical
music - who is the artist? The composer? The conductor? The orchestra? The soloist?
MPEG-7 is vastly overkill from our point of view, and only a tiny part ("The
Collection Structure DS") has anything to say about organising music from our perspective.
MPEG7-Lite as used by the UPnP Audio/Visual framework (
But UPnP is a device-oriented system, where a device (such as a PVR) is responsible for all the individual items stored on it. Although the device may contain a complex directory structure, the individual components of this are not "first class" objects, directly visible and addressable. This would make it hard to, say, set up a "playlist" across a set of devices such as a PVR, an iPod and a home server storing copies of LPs.
The REST community criticises Web services (using SOAP) on the grounds that services have no "addressable endpoint" and that data returned from a service is an XML document that is not addressable at all. UPnP A/V directories are not addressable. In both cases this leads to a loss of flexibility in that clients and services can only work within the bounds of the supplied services and are hence restricted in what they can do - in the case of UPnP it is hard to build up cross-device playlists. So we adopt the extreme viewpoint: every piece of music is advertised as its own service. That allows any other service to build and structure service hierarchies in any way that it wants to. For example, a new service could link photos from an external web site to pieces of music, which would be hard to do with web services or UPnP.
We shall present three servers: one that will just advertise a single piece of music available from an HTTP server, one that will advertise a group of pieces (such as a CD of many pieces) and one that will advertise a collection of groups (such as all the CDs on a disk).
The file server will advertise one file as a service. Details of the file will need to be
stored in a configuration file such as
cant open resources/audio/file/sting.cfg
The server is quite straightforward: it gets information about exporter and service entries
from a configuration file and advertises the source as a service
using a
package audio.httpsource;
import net.jini.lookup.JoinManager;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceID;
import net.jini.discovery.LookupDiscovery;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceRegistrar;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import net.jini.lookup.ServiceIDListener;
import net.jini.lease.LeaseRenewalManager;
import net.jini.discovery.LookupDiscoveryManager;
import net.jini.discovery.DiscoveryEvent;
import net.jini.discovery.DiscoveryListener;
import java.rmi.RMISecurityManager;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.net.URL;
import net.jini.lookup.entry.*;
import net.jini.core.entry.Entry;
import net.jini.core.discovery.LookupLocator;
import net.jini.config.*;
import net.jini.export.*;
import net.jini.id.UuidFactory;
import net.jini.id.Uuid;
import java.io.*;
import audio.http.*;
/**
* FileServer.java
*/
public class FileServer {
// explicit proxy for Jini 2.0
private Remote proxy;
private HttpSourceImpl impl;
private static String configFile;
private Entry[] entries;
private File serviceIDFile;
private ServiceID serviceID;
public static void main(String argv[]) {
configFile = argv[0];
FileServer serv = new FileServer(argv);
// stay around forever
Object keepAlive = new Object();
synchronized(keepAlive) {
try {
keepAlive.wait();
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
// do nothing
}
}
}
public FileServer(String[] argv) {
URL url = null;
Exporter exporter = null;
if (argv.length != 1) {
System.err.println("Usage: FileServer config_file");
System.exit(1);
}
try {
} catch(Exception e) {
System.err.println("New impl: " + e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
String[] configArgs = argv;
try {
// get the configuration (by default a FileConfiguration)
Configuration config = ConfigurationProvider.getInstance(configArgs);
// and use this to construct an exporter
exporter = (Exporter) config.getEntry( "HttpFile",
"exporter",
Exporter.class);
url = (URL) config.getEntry("HttpFile",
"url",
URL.class);
serviceIDFile = (File) config.getEntry("HttpFile",
"serviceIDFile",
File.class);
getOrMakeServiceID(serviceIDFile);
Class cls = Class.forName("[Lnet.jini.core.entry.Entry;");
System.out.println(cls.toString());
entries = (Entry []) config.getEntry("HttpFile",
"entries",
cls);
} catch(Exception e) {
System.err.println(e.toString());
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
// Find the right implementation for the content type
String urlStr = url.toString();
try {
if (urlStr.endsWith("wav")) {
impl = new HttpWAVSourceImpl(url);
} else if (urlStr.endsWith("mp3")) {
impl = new HttpMP3SourceImpl(url);
} else if (urlStr.endsWith("ogg")) {
impl = new HttpOggSourceImpl(url);
} else {
System.out.println("Can't handle presentation type: " +
url);
return;
}
} catch(java.net.MalformedURLException e) {
System.err.println(e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
try {
// export an object of this class
proxy = exporter.export(impl);
} catch(java.rmi.server.ExportException e) {
System.err.println(e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
// install suitable security manager
System.setSecurityManager(new RMISecurityManager());
JoinManager joinMgr = null;
try {
LookupDiscoveryManager mgr =
new LookupDiscoveryManager(LookupDiscovery.ALL_GROUPS,
new LookupLocator[] {
new LookupLocator("jini://jannote.jan.home/")},
// unicast locators
null); // DiscoveryListener
joinMgr = new JoinManager(proxy, // service proxy
entries, // attr sets
serviceID, // ServiceID
mgr, // DiscoveryManager
new LeaseRenewalManager());
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
private void getOrMakeServiceID(File serviceIDFile) {
// try to read the service ID as
// object from the file
serviceID = null;
try {
ObjectInputStream ois =
new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(serviceIDFile));
serviceID = (ServiceID) ois.readObject();
System.out.println("Got dir service id " + serviceID);
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("Couldn't get service IDs - generating new one");
try {
ObjectOutputStream oos =
new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(serviceIDFile));
Uuid uuid = UuidFactory.generate();
serviceID = new ServiceID(uuid.getMostSignificantBits(),
uuid.getLeastSignificantBits());
oos.writeObject(serviceID);
oos.close();
} catch(Exception e2) {
System.out.println("Couldn't save ids");
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
} // FileServer
The file source server requires the following classes
All the classes in the
java -classpath audio.httpsource.FileServer.jar audio.httpsource.FileServer sting.cfg
Much music comes on CDs, on LPs, tapes or cassettes, or in some similarly structured format (even a radio show has a structure). This structure often mirrors that of a "directory". So a CD might contains a directory of tracks, and so on. A directory can be a service in its own right, so there is an interface to define it.
/**
* Directory.java
*/
package audio.common;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceID;
/**
* A one-level directory of services. If the directory is also
*/
public interface Directory extends Remote {
ServiceID[] getServiceIDs() throws RemoteException;
}// Directory
While a directory can hold any type of service, we will only look at a directory that
contains sound file services available from an HTTP server. The minimal description
for each service is then its URL (so that a service can be constructed) and a service
ID so that it can be part of the directory. The set of URLs is given in an array of
trackURLs in a configuration, and the service IDs are stored as
objects in a file referenced by the same configuration. Additional information
such as the name of the directory can be given as an
import net.jini.jeri.BasicILFactory;
import net.jini.jeri.BasicJeriExporter;
import net.jini.jeri.tcp.TcpServerEndpoint;
import java.net.URL;
import net.jini.core.entry.Entry;
import net.jini.lookup.entry.*;
import com.sun.jini.config.ConfigUtil;
import java.io.File;
HttpFileSourceServer {
exporter = new BasicJeriExporter(TcpServerEndpoint.getInstance(0),
new BasicILFactory());
serviceIDFile = new File("soundfiles/clapton.ids");
entries = new Entry[] {new Name("Eric Clapton / Unplugged")
};
cdIndexDiscID = "H2WKL5utOWh9nlMK6S3y537vygQ-";
cddbDiscID = "cb0e7b0e";
localhost = ConfigUtil.getHostName();
urlBase = ConfigUtil.concat(new String[] {
"http://",
localhost,
"/soundfiles/clapton/"
}
);
trackURLs = new URL[] {
new URL(ConfigUtil.concat(new String[] {
urlBase,
"audio_01.ogg"
}
)
),
new URL(ConfigUtil.concat(new String[] {
urlBase,
"audio_02.ogg"
}
)
),
new URL(ConfigUtil.concat(new String[] {
urlBase,
"audio_03.ogg"
}
)
)
};
trackNames = new String[] {
"Signe",
"Before You Accuse Me",
"Hey Hey"
};
}
This server is a bit of a departure from previous ones in this book: it creates and
advertises a number of services, not just one. Each service will need to respond to
its own requests and not to those of others. So each one will need to have a separate
dispatcher for its own requests. This is done quite simply by exporting each service
by a separate exporter - in fact this is a requirement, as an exporter can only one
service. However, the servers we have looked at have typically had a
A single
/**
* DirectoryServerOpt.java
*/
package audio.httpsource;
import common.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import net.jini.lookup.JoinManager;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceID;
import net.jini.lease.LeaseRenewalManager;
import net.jini.lookup.entry.*;
import net.jini.core.entry.Entry;
import java.rmi.RMISecurityManager;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import net.jini.core.discovery.LookupLocator;
import net.jini.discovery.LookupDiscovery;
import java.net.URL;
import net.jini.discovery.LookupDiscoveryManager;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import net.jini.lookup.ServiceIDListener;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceID;
import net.jini.discovery.DiscoveryEvent;
import net.jini.discovery.DiscoveryListener;
import net.jini.core.lookup.*;
import net.jini.core.lease.*;
import net.jini.id.UuidFactory;
import net.jini.id.Uuid;
import net.jini.config.*;
import net.jini.export.*;
import com.sun.jini.config.Config;
import java.util.Vector;
import audio.common.Directory;
import audio.http.*;
import audio.transport.*;
public class DirectoryServerOpt implements Directory, DiscoveryListener {
private ServiceID serviceID = null;
private ServiceID[] serviceIDs;
protected Remote proxy;
protected HttpSourceImpl impl;
private Entry[] dirEntries;
private String cdInfo;
// info pulled out of a Configuration
private URL url = null;
private Exporter exporter = null;
private String cdIndexDiscID;
private String cddbDiscID;
private URL[] trackURLs;
private String[] trackNames;
private Configuration config;
private File serviceIDFile;
// JoinManager's to keep the services alive
// private JoinManager[] joinMgrs;
// private JoinManager dirJoinMgr;
private LeaseRenewalManager leaseRenewalManager;
private LookupDiscoveryManager mgr;
private Vector sources = new Vector();
public DirectoryServerOpt(String[] configArgs,
LeaseRenewalManager leaseRenewalManager,
LookupDiscoveryManager lookupDiscoveryManager) {
this.leaseRenewalManager = leaseRenewalManager;
this.mgr = lookupDiscoveryManager;
System.out.println("1");
getConfiguration(configArgs);
System.out.println("2");
cdInfo = getCDInfo();
System.out.println("3");
// joinMgrs = new JoinManager[trackURLs.length];
System.out.println("4");
/*
try {
mgr = new LookupDiscoveryManager(LookupDiscovery.ALL_GROUPS,
//new LookupLocator[] {
// new LookupLocator("jini://jannote.jan.home/")},
null,
// unicast locators
this); // DiscoveryListener
} catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
*/
mgr.addDiscoveryListener(this);
}
public void discovered(DiscoveryEvent e) {
ServiceRegistrar[] regs = e.getRegistrars();
for (int m = 0; m < regs.length; m++) {
ServiceRegistrar reg = regs[m];
System.out.println("5");
for (int n = 0; n < trackURLs.length; n++) {
makeFileService(reg, n, trackURLs[n]);
}
makeDirService(reg);
}
}
public void discarded(DiscoveryEvent e) {
}
public ServiceID[] getServiceIDs() throws RemoteException {
return serviceIDs;
}
private void getConfiguration(String[] configArgs) {
try {
// get the configuration (by default a FileConfiguration)
// in configArgs[0]
config = ConfigurationProvider.getInstance(configArgs);
System.out.println("Config is " + config);
} catch(Exception e) {
System.err.println(e.toString());
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
try {
Class cls = Entry[].class;
System.out.println(cls.toString());
dirEntries = (Entry []) config.getEntry("HttpFileSourceServer",
"entries",
cls);
} catch(Exception e) {
System.err.println("Config error: " + e.toString());
}
try {
cdIndexDiscID = (String) config.getEntry("HttpFileSourceServer",
"cdIndexDiscID",
String.class);
} catch(Exception e) {
System.err.println("Config error: " + e.toString());
}
try {
// This is an unsigned long - sometimes too big for Java long
cddbDiscID = (String) config.getEntry("HttpFileSourceServer",
"cddbDiscID",
String.class,
null);
} catch(Exception e) {
System.err.println("Config error: " + e.toString());
}
try {
Class cls = URL[].class;
System.out.println(cls.toString());
trackURLs = (URL []) config.getEntry("HttpFileSourceServer",
"trackURLs",
cls);
} catch(Exception e) {
System.err.println("Config error: " + e.toString());
trackURLs = new URL[] {};
}
try {
Class cls = String[].class;
System.out.println(cls.toString());
trackNames = (String []) config.getEntry("HttpFileSourceServer",
"trackNames",
cls);
} catch(Exception e) {
System.err.println("Config error: " + e.toString());
}
try {
serviceIDFile = (File) config.getEntry("HttpFileSourceServer",
"serviceIDFile",
File.class);
getOrMakeServiceIDs(serviceIDFile);
} catch(Exception e) {
System.err.println("Config error: " + e.toString());
}
}
private void getOrMakeServiceIDs(File serviceIDFile) {
// try to read all the service IDs as
// objects from the file
serviceIDs = new ServiceID[trackURLs.length];
try {
ObjectInputStream ois =
new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(serviceIDFile));
serviceID = (ServiceID) ois.readObject();
System.out.println("Got dir service id " + serviceID);
for (int n = 0; n < trackURLs.length; n++) {
serviceIDs[n] = (ServiceID) ois.readObject();
System.out.println("Got service id " + serviceIDs[n]);
}
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("Couldn't get service IDs - generating new ones");
try {
ObjectOutputStream oos =
new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(serviceIDFile));
Uuid uuid = UuidFactory.generate();
serviceID = new ServiceID(uuid.getMostSignificantBits(),
uuid.getLeastSignificantBits());
oos.writeObject(serviceID);
for (int n = 0; n < serviceIDs.length; n++) {
Uuid uuidFile = UuidFactory.generate();
ServiceID id = new ServiceID(uuidFile.getMostSignificantBits(),
uuidFile.getLeastSignificantBits());
oos.writeObject(id);
serviceIDs[n] = id;
System.out.println("Generating service id " + serviceIDs[n]);
}
} catch(Exception e2) {
System.out.println("Couldn't save ids");
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void makeDirService(ServiceRegistrar registrar) {
try {
exporter = (Exporter) config.getEntry( "HttpFileSourceServer",
"exporter",
Exporter.class);
} catch(Exception e) {
System.err.println(e.toString());
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
try {
System.out.println("Export dir using exporter " + exporter);
// export an object of this class
proxy = exporter.export(this);
} catch(java.rmi.server.ExportException e) {
System.err.println(e.toString());
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
ServiceRegistration sr = null;
try {
sr = registrar.register(new ServiceItem(serviceID,
proxy,
dirEntries),
Lease.FOREVER);
} catch(RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
leaseRenewalManager.renewUntil(sr.getLease(), Lease.FOREVER, null);
// dirJoinMgr = registerService(proxy, serviceID, dirEntries);
}
private void makeFileService(ServiceRegistrar registrar, int index, URL url) {
Exporter exporter = null;
try {
exporter = (Exporter) config.getEntry( "HttpFileSourceServer",
"exporter",
Exporter.class);
} catch(Exception e) {
System.err.println(e.toString());
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
String urlStr = url.toString();
System.out.println("URL is " + urlStr);
try {
if (urlStr.endsWith("wav")) {
impl = new HttpWAVSourceImpl(url);
} else if (urlStr.endsWith("mp3")) {
impl = new HttpMP3SourceImpl(url);
} else if (urlStr.endsWith("ogg")) {
impl = new HttpOggSourceImpl(url);
} else {
System.out.println("Can't handle presentation type: " +
url);
return;
}
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
sources.add(impl);
try {
System.out.println("Export file " + url + " using exporter " + exporter);
// export an object of this class
proxy = exporter.export(impl);
} catch(java.rmi.server.ExportException e) {
System.err.println(e.toString());
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
String trackInfo = getTrackInfo(index);
Entry[] entries = new Entry[] {new Name(trackInfo)};
// joinMgrs[index] = registerService(proxy, serviceIDs[index], entries);
ServiceRegistration sr = null;
try {
sr = registrar.register(new ServiceItem(serviceIDs[index],
proxy,
entries),
Lease.FOREVER);
} catch(RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
leaseRenewalManager.renewUntil(sr.getLease(), Lease.FOREVER, null);
}
private JoinManager registerService(Remote proxy, ServiceID serviceID, Entry[] entries) {
JoinManager joinMgr = null;
try {
System.out.println("Registering with id " + serviceID);
joinMgr = new JoinManager(proxy, // service proxy
entries, // attr sets
serviceID, // ServiceID
mgr, // DiscoveryManager
leaseRenewalManager);
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
return joinMgr;
}
public String getTrackInfo(int index) {
// get from trackNames if possible
if (trackNames != null) {
if ((trackNames.length > index) &&
(trackNames[index] != null)) {
return(cdInfo + ": " + trackNames[index]);
}
}
// failing that, get from CDDB d/b if possible
// ... not yet implemented
// failing that...
String indexStr = null;
if (index < 9) indexStr = "0" + (index + 1);
else indexStr = "" + (index + 1);
return(cdInfo + ": Track " + indexStr);
}
public String getCDInfo() {
// get from CDDB d/b if possible
// failing that...
if (dirEntries == null) {
return "";
}
for (int n = 0; n < dirEntries.length; n++) {
if (dirEntries[n] instanceof Name) {
return ((Name) dirEntries[n]).name;
}
}
return "";
}
public static void main(String[] argv) {
LeaseRenewalManager leaseRenewalManager = new LeaseRenewalManager();
LookupDiscoveryManager lookupDiscoveryManager = null;
try {
lookupDiscoveryManager =
new LookupDiscoveryManager(LookupDiscovery.ALL_GROUPS,
//new LookupLocator[] {
// new LookupLocator("jini://jannote.jan.home/")},
null, // unicast locators
null); // DiscoveryListener
} catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
// install suitable security manager
System.setSecurityManager(new RMISecurityManager());
DirectoryServerOpt ds = new DirectoryServerOpt(argv,
leaseRenewalManager,
lookupDiscoveryManager);
// stay around forever
Object keepAlive = new Object();
synchronized(keepAlive) {
try {
keepAlive.wait();
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
// do nothing
}
}
}
}// DirectoryServer
The final source server that we shall build generalises the idea of a "set of CDs", by
looking at a set of directories. If a set of configurations are each stored in files in
a common directory, then by running through the directory and advertising each directory
we will have advertised the entire set. This server takes a directory name as command line
argument and creates a new
/**
* DirDirectoryServer.java
*/
package audio.httpsource;
import common.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.rmi.RMISecurityManager;
import java.util.Vector;
import net.jini.lease.LeaseRenewalManager;
import net.jini.discovery.LookupDiscoveryManager;
import net.jini.discovery.LookupDiscovery;
/**
* Read a (file) directory for a list of .cfg files
*/
public class DirDirectoryServer {
private Vector dirs = new Vector();
public DirDirectoryServer(String dirStr) {
LeaseRenewalManager leaseRenewalManager = new LeaseRenewalManager();
LookupDiscoveryManager lookupDiscoveryManager = null;
try {
lookupDiscoveryManager =
new LookupDiscoveryManager(LookupDiscovery.ALL_GROUPS,
//new LookupLocator[] {
// new LookupLocator("jini://jannote.jan.home/")},
null, // unicast locators
null); // DiscoveryListener
} catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
File dir = new File(dirStr);
String[] files = dir.list(new java.io.FilenameFilter() {
public boolean accept(File d, String name) {
System.out.println("Checking file " + name);
if (name.endsWith(".cfg"))
return true;
else
return false;
}
});
System.out.println("Dir length: " + files.length);
for (int n = 0; n < files.length; n++) {
dirs.add(
new DirectoryServerOpt(new String[] {dirStr + "/" + files[n]},
leaseRenewalManager,
lookupDiscoveryManager)
);
}
}
public static void main(String[] argv) {
System.setSecurityManager(new RMISecurityManager());
DirDirectoryServer dd = new DirDirectoryServer(argv[0]);
// stay around forever
Object keepAlive = new Object();
synchronized(keepAlive) {
try {
keepAlive.wait();
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
// do nothing
}
}
}
}// DirDirectoryServer
A client will locate sources and sinks and allow a user to make selections
from them. Each sink will be told about the selected sources, and each source
will be told about the selected sinks. The client may register itself as
a listener for events (such as STOP) from the services.
Then the client will ask the sources to play() and the
sinks to record().
A really basic client will just find a sink and a source (any source, any sink), tell each other about the other and then play/record to audio stream. This can be done by
package audio.client;
import java.rmi.RMISecurityManager;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import net.jini.discovery.LookupDiscovery;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceTemplate;
import net.jini.discovery.LookupDiscoveryManager;
import net.jini.lookup.ServiceDiscoveryManager;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceItem;
import net.jini.lease.LeaseRenewalManager;
import audio.common.Sink;
import audio.common.Source;
/**
* BasicClient.java
*/
public class BasicClient {
private static final long WAITFOR = 100000L;
private ServiceDiscoveryManager clientMgr = null;
public static void main(String argv[]) {
new BasicClient();
// stay around long enough to receive replies
try {
Thread.currentThread().sleep(2*WAITFOR);
} catch(java.lang.InterruptedException e) {
// do nothing
}
}
public BasicClient() {
System.setSecurityManager(new RMISecurityManager());
try {
LookupDiscoveryManager mgr =
new LookupDiscoveryManager(LookupDiscovery.ALL_GROUPS,
null, // unicast locators
null); // DiscoveryListener
clientMgr = new ServiceDiscoveryManager(mgr,
new LeaseRenewalManager());
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
// find a source and sink
Sink sink = (Sink) getService(Sink.class);
Source source = (Source) getService(Source.class);
// tell them about each other
try {
source.addSink(sink);
sink.addSource(source);
} catch(Exception e) {
System.err.println("Error setting source or sink " + e);
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
// play the audio
try {
System.out.println("Playing...");
source.play();
sink.record();
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error in playing " + e);
System.exit(1);
}
}
private Object getService(Class cls) {
Class [] classes = new Class[] {cls};
ServiceTemplate template = new ServiceTemplate(null, classes,
null);
ServiceItem item = null;
// Try to find the service, blocking till timeout if necessary
try {
item = clientMgr.lookup(template,
null, // no filter
WAITFOR); // timeout
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
if (item == null) {
// couldn't find a service in time
System.out.println("no service for class " + cls);
System.exit(1);
}
// Return the service
return item.service;
}
} // BasicClient
The basic client requires the following classes
All the classes in the
java -classpath audio.client.BasicClient.jar audio.client.BasicClient
A more complex client will monitor the sinks and sources (and directories)
and display them in suitable panels.
These panels will allow selections of sources and sink. The GUIClient looks
after service management.
/**
* GUIClient.java
*/
package audio.client;
import java.rmi.RMISecurityManager;
import net.jini.discovery.LookupDiscovery;
import net.jini.lookup.ServiceDiscoveryListener;
import net.jini.lookup.ServiceDiscoveryEvent;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceTemplate;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceItem;
import net.jini.lookup.ServiceDiscoveryManager;
import net.jini.discovery.LookupDiscoveryManager;
import net.jini.lease.LeaseRenewalManager;
import net.jini.lookup.LookupCache;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceID;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import net.jini.lookup.ServiceItemFilter;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceTemplate;
import net.jini.config.*;
import net.jini.export.*;
import audio.common.*;
/**
* An A/V client that monitors sources and sinks and
*/
public class GUIClient implements ServiceDiscoveryListener {
private static final long WAITFOR = 100000L;
private ClientFrame clientFrame;
private LookupCache cache;
private ServiceDiscoveryManager clientMgr;
private static String CONFIG_FILE = "resources/audio/jeri/http_sink_server.config";
public static void main(String argv[]) {
ClientFrame cf = new ClientFrame();
GUIClient client = new GUIClient(cf);
cf.setClient(client);
cf.setSize(600, 600);
cf.setVisible(true);
/*
// stay around long enough to receive replies
try {
Thread.currentThread().sleep(100000L);
} catch(java.lang.InterruptedException e) {
// do nothing
}
*/
}
public GUIClient(ClientFrame cf) {
clientFrame = cf;
System.setSecurityManager(new RMISecurityManager());
try {
LookupDiscoveryManager mgr =
new LookupDiscoveryManager(LookupDiscovery.ALL_GROUPS,
null, // unicast locators
null); // DiscoveryListener
clientMgr = new ServiceDiscoveryManager(mgr,
new LeaseRenewalManager());
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
ServiceTemplate template = new ServiceTemplate(null, null,
null);
try {
cache = clientMgr.createLookupCache(template,
null, // no filter
this); // listener
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
// methods for ServiceDiscoveryListener
public void serviceAdded(ServiceDiscoveryEvent evt) {
// evt.getPreEventServiceItem() == null
ServiceItem postItem = evt.getPostEventServiceItem();
System.out.println("Service appeared: " +
postItem.service.getClass().toString());
if (postItem.service instanceof Directory) {
System.out.println(" is dir");
addDirectory(postItem);
}
if (postItem.service instanceof Sink) {
System.out.println(" is sink");
clientFrame.addSink(postItem);
}
if (postItem.service instanceof Source) {
System.out.println(" is source");
clientFrame.addSource(postItem);
}
}
public void serviceChanged(ServiceDiscoveryEvent evt) {
ServiceItem preItem = evt.getPostEventServiceItem();
ServiceItem postItem = evt.getPreEventServiceItem() ;
System.out.println("Service changed: " +
postItem.service.getClass().toString());
}
public void serviceRemoved(ServiceDiscoveryEvent evt) {
// evt.getPostEventServiceItem() == null
ServiceItem preItem = evt.getPreEventServiceItem();
System.out.println("Service disappeared: " +
preItem.service.getClass().toString());
if (preItem.service instanceof Directory) {
System.out.println(" was dir");
clientFrame.removeDirectory(preItem);
}
if (preItem.service instanceof Sink) {
System.out.println(" was sink");
clientFrame.removeSink(preItem);
}
if (preItem.service instanceof Source) {
System.out.println(" was source");
clientFrame.removeSource(preItem);
}
}
private void addDirectory(ServiceItem item) {
Object node = clientFrame.addDirectory(item);
ServiceID[] ids = null;
try {
ids = ((Directory) item.service).getServiceIDs();
} catch(RemoteException e) {
System.err.println(e.toString());
return;
}
for (int n = 0; n < ids.length; n++) {
/* My directories register all component services before themselves,
* so when the LUS gets the directory, it already has its contents.
* I asssumed that the LUS would give them to the ServiceDiscoveryManager
* with order preserved, so by the time the cache says it has a directory
* then it will already have the components. Experimentally, this ain't so.
* So we ask the discovery manager for a search instead
*/
ServiceID id = ids[n];
ServiceTemplate tmpl = new ServiceTemplate(id, null, null);
ServiceItem dirItem = null;
try {
dirItem = clientMgr.lookup(tmpl, null, WAITFOR);
} catch (Exception e) {
// dirItem stays null
}
/* Broken: see above
final ServiceID id = ids[n];
// find a service in the cache that matches the service ID
// we are looking for - doesn't seem to be a way to retrieve
// by serviceID
ServiceItemFilter filter = new ServiceItemFilter() {
public boolean check(ServiceItem dirItem) {
if (dirItem.serviceID.equals(id)) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
};
ServiceItem dirItem = cache.lookup(filter);
*/
if (dirItem != null) {
clientFrame.addDirectoryElement(node, dirItem);
} else {
System.out.println("Adding to dir " + item.serviceID +
": couldn't find dir element " + id);
}
}
}
public Remote export(PlayFrame cf) {
String[] configArgs = new String[] {CONFIG_FILE};
Remote proxy;
try {
// get the configuration (by default a FileConfiguration)
Configuration config = ConfigurationProvider.getInstance(configArgs);
// and use this to construct an exporter
Exporter exporter = (Exporter) config.getEntry( "HttpSinkServer",
"exporter",
Exporter.class);
// export an object for the client listener
proxy = exporter.export(cf);
return proxy;
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
} // GUIClient
The ClientFrame looks after display and selection of sources/directories/sinks.
It shows each of these in Swing JTabbedPane. The directory information
is displayed using a JTree (this is good for playing a CD in track order).
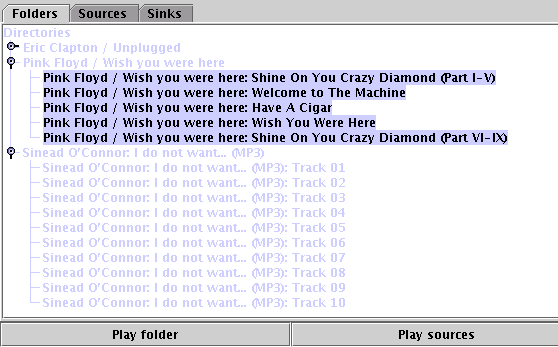
JList with the services alphabetically sorted.
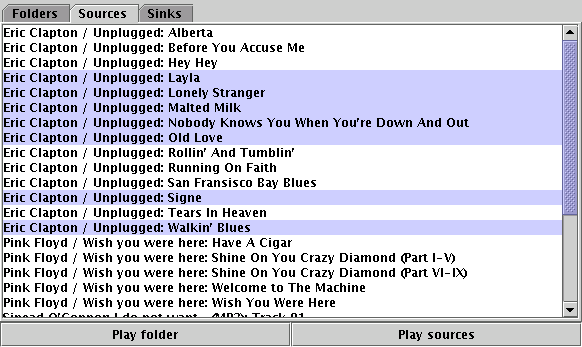
JList.
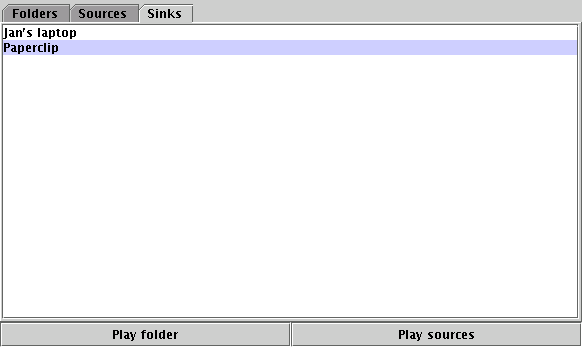
The ClientFrame is
/**
* ClientFrame.java
*/
package audio.client;
import audio.common.*;
import net.jini.core.entry.Entry;
import net.jini.lookup.entry.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.tree.*;
import javax.swing.event.*;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceItem;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceID;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import net.jini.core.event.RemoteEvent;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import net.jini.core.event.RemoteEventListener;
import java.rmi.MarshalledObject;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* The main Swing JFrame for the GUIClient
*/
public class ClientFrame extends JFrame
implements ActionListener,
ListSelectionListener,
TreeSelectionListener,
TreeExpansionListener,
RemoteEventListener {
private GUIClient client;
private JList sources = new JList();
private JList sinks = new JList();
private JTree directories = new JTree();
private JButton playFolderBtn = new JButton("Play folder");
private JButton playSourcesBtn = new JButton("Play sources");
private JButton stopBtn = new JButton("Stop");
private Remote proxy;
public ClientFrame() {
super("Audio Router");
makeLayout();
addListeners();
setupLists();
}
public void setClient(GUIClient client) {
this.client = client;
}
private void makeLayout() {
Container contentPane = getContentPane();
contentPane.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JPanel bottom = new JPanel();
JTabbedPane top = new JTabbedPane();
contentPane.add(bottom, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
contentPane.add(top, BorderLayout.CENTER);
JPanel dirPane = new JPanel();
JPanel sourcePane = new JPanel();
JPanel sinkPane = new JPanel();
top.add("Folders", dirPane);
top.add("Sources", sourcePane);
top.add("Sinks", sinkPane);
dirPane.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JScrollPane js0 = new JScrollPane();
js0.getViewport().setView(directories);
dirPane.add(js0,
BorderLayout.CENTER);
sourcePane.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JScrollPane js1 = new JScrollPane();
js1.getViewport().setView(sources);
sourcePane.add(js1,
BorderLayout.CENTER);
sinkPane.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JScrollPane js2 = new JScrollPane();
js2.getViewport().setView(sinks);
sinkPane.add(js2, BorderLayout.CENTER);
bottom.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JPanel buttons = new JPanel();
buttons.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 3));
buttons.add(playFolderBtn);
buttons.add(playSourcesBtn);
// buttons.add(stopBtn);
bottom.add(buttons, BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
private void addListeners() {
playFolderBtn.addActionListener(this);
playSourcesBtn.addActionListener(this);
stopBtn.addActionListener(this);
directories.addTreeSelectionListener(this);
directories.addTreeExpansionListener(this);
sources.addListSelectionListener(this);
sinks.addListSelectionListener(this);
}
private void setupLists() {
LabelCellRenderer labelRend = new LabelCellRenderer();
directories.setCellRenderer(labelRend);
DefaultMutableTreeNode root = new DefaultMutableTreeNode("Directories");
directories.setModel(new DefaultTreeModel(root));
sources.setCellRenderer(labelRend);
sources.setModel(new DefaultListModel());
sinks.setCellRenderer(labelRend);
sinks.setModel(new DefaultListModel());
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) {
Object[] sourceSels = null;
if (evt.getSource() == playSourcesBtn) {
sourceSels = sources.getSelectedValues();
} else if (evt.getSource() == playFolderBtn) {
TreePath[] selectionPaths = directories.getSelectionPaths();
if (selectionPaths == null) {
sourceSels = null;
} else {
sourceSels = new Object[selectionPaths.length];
for (int n = 0; n < sourceSels.length; n++) {
DefaultMutableTreeNode node = (DefaultMutableTreeNode)
selectionPaths[n].
getLastPathComponent();
Object lastComponent = node.getUserObject();
sourceSels[n] = lastComponent;
}
}
}
if ((sourceSels == null) || (sourceSels.length == 0)) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,
"No source selected", "Source is null",
JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
Object[] sinkSels = sinks.getSelectedValues();
if ((sinkSels == null) || (sinkSels.length == 0)) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,
"No sink selected", "Sink is null",
JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
ServiceItem[] sourceSelections = new ServiceItem[sourceSels.length];
for (int n = 0; n < sourceSels.length; n++) {
sourceSelections[n] = (ServiceItem) sourceSels[n];
}
ServiceItem[] sinkSelections = new ServiceItem[sinkSels.length];
for (int n = 0; n < sinkSels.length; n++) {
sinkSelections[n] = (ServiceItem) sinkSels[n];
}
// Sink sink = (Sink) sinkSelections[0].service;
new PlayFrame(client).play(sourceSelections, sinkSelections[0]);
// play(sourceSelections, sinkSelections[0]);
}
private void play(ServiceItem[] sourceSelections, ServiceItem sinkItem) {
if ((sourceSelections == null) || (sourceSelections.length == 0)) {
System.out.println("Play: null sources");
return;
}
Source source = (Source) sourceSelections[0].service;
Sink sink = (Sink) sinkItem.service;
ServiceItem[] rest = new ServiceItem[sourceSelections.length - 1];
for (int n = 0; n < rest.length; n++) {
rest[n] = sourceSelections[n + 1];
}
MarshalledObject handback = null;
try {
handback = new MarshalledObject(new SourceSink(rest, sinkItem));
} catch(java.io.IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
try {
if (proxy == null) {
// proxy = client.export(this);
}
// source.addSourceListener((RemoteEventListener) proxy, null);
System.out.println("Added source " + source + " proxy " + proxy);
sink.addSinkListener((RemoteEventListener) proxy, handback);
System.out.println("Added sink " + sink + " proxy " + proxy + " handback " +
((SourceSink) handback.get()).sources);
} catch(RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try{
System.out.println("Setting sink to: " + sink);
source.addSink(sink);
System.out.println("Setting source to: " + source);
sink.addSource(source);
System.out.println("Playing " + sourceSelections[0].attributeSets[0]);
// and then play...
source.play();
sink.record();
} catch(AlreadyPlayingException e) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,
"Source already playing",
"Play error",
JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
} catch(AlreadyRecordingException e) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,
"Sink already recording",
"Record error",
JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
} catch(Exception e) {
// IncompatableSink/Source
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void stop(ServiceItem[] sourceSelections, ServiceItem sinkItem) {
// Source source = (Source) sourceSelections[0].service;
System.out.println("Stopping");
Sink sink = (Sink) sinkItem.service;
try{
// source.stop();
sink.stop();
/*
} catch(NotPlayingException e) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,
"Source not playing",
"Play stop error",
JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
*/
} catch(NotRecordingException e) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,
"Sink not recording",
"Record stop error",
JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
} catch(Exception e) {
// ignore?
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void notify(RemoteEvent evt) {
Object src = evt.getSource();
System.out.println("Updating " + src);
if ((src instanceof Sink) &&
(evt.getID() == Sink.STOP)) {
System.out.println("Sink stopped event");
Sink sink = (Sink) src;
try {
sink.removeSinkListener((RemoteEventListener) proxy);
} catch(RemoteException e) {
// ignore
} catch(NoSuchListenerException e) {
// ignore
}
MarshalledObject handback = evt.getRegistrationObject();
SourceSink ss = null;
try {
ss = (SourceSink) handback.get();
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
ServiceItem[] sources = ss.sources;
ServiceItem sinkItem = ss.sink;
System.out.println(" stop -> play: sources " + sources + " sink " + sink);
play(sources, sinkItem);
} else if ((src instanceof Source) &&
(evt.getID() == Source.STOP)) {
System.out.println("Source stopped event");
}
}
/**********************************
* Source tree manipulation methods
*/
public void valueChanged(TreeSelectionEvent evt) {
JTree tree = (JTree) evt.getSource();
TreePath selectionPath = tree.getSelectionPath();
if (selectionPath == null) {
return;
}
DefaultMutableTreeNode node = (DefaultMutableTreeNode) selectionPath.
getLastPathComponent();
Object lastComponent = node.getUserObject();
System.out.println("Selection: " + lastComponent.toString());
if ( ! node.isLeaf()) {
// select all children of this node
TreePath[] childPaths = new TreePath[node.getChildCount()];
Object[] selPathObjects = selectionPath.getPath();
int selPathObjectsLength = selPathObjects.length;
int n = 0;
Enumeration children = node.children();
while (children.hasMoreElements()) {
Object[] childPathObjects = new Object[selPathObjectsLength + 1];
for (int m = 0; m < selPathObjectsLength; m++) {
childPathObjects[m] = selPathObjects[m];
}
childPathObjects[selPathObjectsLength] = children.nextElement();
childPaths[n++] = new TreePath(childPathObjects);
}
tree.setSelectionPaths(childPaths);
}
}
public void treeCollapsed(TreeExpansionEvent evt) {
System.out.println("Tree collapsed " + evt.getPath());
}
public void treeExpanded(TreeExpansionEvent evt) {
System.out.println("Tree expanded " + evt.getPath());
}
public DefaultMutableTreeNode addDirectory(ServiceItem item) {
DefaultTreeModel model = (DefaultTreeModel) directories.getModel();
DefaultMutableTreeNode newNode =
addDirectoryTreeNode(new ComparableServiceItem(item), model);
return newNode;
}
public void addDirectoryElement(Object node, ServiceItem item) {
final DefaultMutableTreeNode parentNode = (DefaultMutableTreeNode) node;
final DefaultMutableTreeNode newNode =
new DefaultMutableTreeNode(new ComparableServiceItem(item));
Runnable addDirElmt = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
parentNode.add(newNode);
}
};
// Swing isn't thread-safe: all model changes
// have to be placed in the event queue
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(addDirElmt);
}
public void removeDirectory(ServiceItem item) {
DefaultTreeModel model = (DefaultTreeModel) directories.getModel();
removeTreeItem(new ComparableServiceItem(item), model);
}
private DefaultMutableTreeNode addDirectoryTreeNode(final ComparableServiceItem item,
final DefaultTreeModel model) {
final DefaultMutableTreeNode newNode = new DefaultMutableTreeNode(item);
Runnable insertElement = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("Inserting dir tree node " + item);
DefaultMutableTreeNode root = (DefaultMutableTreeNode) model.getRoot();
Enumeration elmts = root.children();
int n = 0;
while (elmts.hasMoreElements()) {
DefaultMutableTreeNode node = (DefaultMutableTreeNode) elmts.nextElement();
if (item.compareTo(node.getUserObject()) <= 0) {
break;
}
n++;
}
model.insertNodeInto(newNode, root, n);
}
};
try {
// Swing isn't thread-safe: all model changes
// have to be placed in the event queue
SwingUtilities.invokeAndWait(insertElement);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return newNode;
}
private DefaultMutableTreeNode removeTreeItem(final ComparableServiceItem item,
final DefaultTreeModel model) {
final DefaultMutableTreeNode newNode = new DefaultMutableTreeNode(item);
Runnable removeElement = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("Removing tree node " + item);
DefaultMutableTreeNode root = (DefaultMutableTreeNode) model.getRoot();
Enumeration elmts = root.children();
DefaultMutableTreeNode foundNode = null;
while (elmts.hasMoreElements()) {
DefaultMutableTreeNode node = (DefaultMutableTreeNode) elmts.nextElement();
if (item.compareTo(node.getUserObject()) == 0) {
System.out.println("Removing directory");
node.removeFromParent();
return;
}
}
System.out.println("Failed to remove directory");
}
};
try {
// Swing isn't thread-safe: all model changes
// have to be placed in the event queue
SwingUtilities.invokeAndWait(removeElement);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return newNode;
}
/**********************************
* Source List manipulation methods
*/
public void addSource(ServiceItem item) {
DefaultListModel model = (DefaultListModel) sources.getModel();
insertListItem(new ComparableServiceItem(item), model);
}
public void removeSource(final ServiceItem item) {
final DefaultListModel model = (DefaultListModel) sources.getModel();
Runnable removeElement = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
if (model.removeElement(new ComparableServiceItem(item))) {
System.err.println("Removed source elmt " + item.service);
} else {
System.err.println("Failed to remove source elmt " + item.service);
}
}
};
// Swing isn't thread-safe: all model changes
// have to be placed in the event queue
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(removeElement);
}
/********************************
* Sink list manipulation methods
*/
public void addSink(ServiceItem item) {
DefaultListModel model = (DefaultListModel) sinks.getModel();
insertListItem(new ComparableServiceItem(item), model);
}
public void removeSink(final ServiceItem item) {
final DefaultListModel model = (DefaultListModel) sinks.getModel();
Runnable removeElement = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
if (model.removeElement(new ComparableServiceItem(item))) {
System.err.println("Removed sink elmt " + item.service);
} else {
System.err.println("Failed to remove sink elmt " + item.service);
}
}
};
// Swing isn't thread-safe: all model changes
// have to be placed in the event queue
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(removeElement);
}
/*********************************
* General list methods
*/
public void valueChanged(ListSelectionEvent evt) {
if (evt.getValueIsAdjusting()) {
return;
}
}
private void insertListItem(final ComparableServiceItem item,
final DefaultListModel model) {
Runnable insertElement = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
Enumeration elmts = model.elements();
int n = 0;
while (elmts.hasMoreElements()) {
if (item.compareTo(elmts.nextElement()) <= 0) {
break;
}
n++;
}
model.add(n, item);
}
};
// there may be other insert's in the event queue, so we can't
// just compare the current list with the item. We have to wait
// till all the pending events have been processed, and then compare
try {
SwingUtilities.invokeAndWait(insertElement);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}// ClientFrame
When source(s) and a sink are selected and a "play" button is pressed, a
PlayFrame is displayed. This shows the currently chosen set of
sources. This frame listens for events from the sink so that it can tell when
a particular track has finished. Then it will start playing the next one.
It gets the information about the "next one" (and all of its successors)
from the "handback" object, which has a list of the remaining tracks to play
/**
* PlayFrame.java
*/
package audio.client;
import audio.common.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import net.jini.core.event.RemoteEvent;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import net.jini.core.event.RemoteEventListener;
import java.rmi.MarshalledObject;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import javax.swing.event.*;
import net.jini.core.entry.Entry;
import net.jini.lookup.ui.MainUI;
import net.jini.lookup.ui.factory.JDialogFactory;
import net.jini.lookup.entry.UIDescriptor;
import net.jini.lookup.ui.attribute.UIFactoryTypes;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.Iterator;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceItem;
/**
* Play a selection of sources to a single sink
*/
public class PlayFrame extends JFrame implements ActionListener,
ChangeListener,
RemoteEventListener {
private ServiceItem[] sources;
private ServiceItem sinkItem;
private Sink sink;
private Source source;
private boolean firstTime = true;
private JList sourceList = new JList();
private JButton stopBtn = new JButton("Stop");
private JButton stopAllBtn = new JButton("Stop all");
private JLabel sinkLabel = new JLabel();
private JSlider sourceVolumeCtl = new JSlider();
private JSlider sinkVolumeCtl = new JSlider();
private DefaultListModel model;
private Remote proxy;
private GUIClient client;
public PlayFrame(GUIClient client) {
setTitle("Player");
this.client = client;
JPanel bottomPanel = new JPanel();
bottomPanel.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
Container contentPane = getContentPane();
contentPane.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
contentPane.add(sinkLabel, BorderLayout.NORTH);
contentPane.add(sourceList, BorderLayout.CENTER);
contentPane.add(bottomPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
JPanel volumeControls = new JPanel();
volumeControls.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 2));
volumeControls.add(sourceVolumeCtl);
volumeControls.add(sinkVolumeCtl);
JPanel buttons = new JPanel();
buttons.setLayout(new GridLayout(1,3));
buttons.add(stopBtn);
buttons.add(stopAllBtn);
bottomPanel.add(volumeControls, BorderLayout.NORTH);
bottomPanel.add(buttons, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
stopBtn.addActionListener(this);
stopAllBtn.addActionListener(this);
LabelCellRenderer labelRend = new LabelCellRenderer();
sourceList.setCellRenderer(labelRend);
model = new DefaultListModel();
sourceList.setModel(model);
sourceVolumeCtl.setEnabled(false);
sinkVolumeCtl.setEnabled(false);
sourceVolumeCtl.addChangeListener(this);
sinkVolumeCtl.addChangeListener(this);
sourceVolumeCtl.setToolTipText("Set volume on the source");
sinkVolumeCtl.setToolTipText("Set volume on the sink");
setSize(400, 300);
setVisible(true);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) {
if (evt.getSource() == stopBtn) {
try {
sink.stop();
sinkVolumeCtl.setEnabled(false);
sourceVolumeCtl.setEnabled(false);
} catch(RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(NotRecordingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else if (evt.getSource() == stopAllBtn) {
/* This doesn;t work right
// kill the rest of the playlist by removing
// our listener and putting in a new one with
// null playback
try {
sink.removeSinkListener((RemoteEventListener) proxy);
System.out.println("Removed listener " + proxy);
sink.addSinkListener((RemoteEventListener) proxy,
new MarshalledObject(
new SourceSink(null, null)));
System.out.println("Added listener with null playback");
} catch(RemoteException e) {
// ignore
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(NoSuchListenerException e) {
System.err.println("Can't change listener " + proxy);
} catch(IOException e) {
System.err.println("Can't marshall null " + proxy);
}
*/
// to fix above... when the stop event arrives, we will try to play but just terminate
sources = null;
// now stop the play
try {
sink.stop();
sinkVolumeCtl.setEnabled(false);
sourceVolumeCtl.setEnabled(false);
} catch(RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(NotRecordingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void stateChanged(ChangeEvent e) {
JSlider slider = (JSlider) e.getSource();
int vol = slider.getValue();
VolumeControl volCtl = null;
if (slider == sinkVolumeCtl) {
volCtl = (VolumeControl) sink;
} else if (slider == sourceVolumeCtl) {
volCtl = (VolumeControl) source;
}
try {
volCtl.setVolume(vol);
} catch(RemoteException ex) {
// ignore
}
}
public void play(ServiceItem[] sources, ServiceItem sinkItem) {
if ((sources == null) || (sources.length == 0)) {
System.out.println("Play: null sources");
// dispose();
Runnable doDispose = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
dispose();
}
};
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(doDispose);
return;
}
this.sources = sources;
this.sinkItem = sinkItem;
sink = (Sink) sinkItem.service;
source = (Source) sources[0].service;
sinkLabel.setText("Playing to " + sinkItem.toString());
model.clear();
for (int n = 0; n < sources.length; n++) {
model.addElement(sources[n]);
}
// just give the event source something it can put in a table
MarshalledObject handback = null;
try {
handback = new MarshalledObject(null);
} catch(java.io.IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
/*
ServiceItem[] rest = new ServiceItem[sources.length - 1];
for (int n = 0; n < rest.length; n++) {
rest[n] = sources[n + 1];
}
MarshalledObject handback = null;
try {
handback = new MarshalledObject(new SourceSink(rest, sinkItem));
} catch(java.io.IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
*/
try {
// this is a bit of a hack
if (firstTime) {
if (proxy == null) {
proxy = client.export(this);
}
// source.addSourceListener((RemoteEventListener) proxy, null);
System.out.println("Added source " + source + " proxy " + proxy);
sink.addSinkListener((RemoteEventListener) proxy, handback);
System.out.println("Added sink " + sink + " proxy " + proxy + " handback " +
"null" /*((SourceSink) handback.get()).sources*/ );
firstTime = false;
}
} catch(RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try{
System.out.println("Setting sink to: " + sink);
source.addSink(sink);
System.out.println("Setting source to: " + source);
sink.addSource(source);
System.out.println("Playing" + sources[0].attributeSets[0]);
// check for UI elements
checkUI(sinkItem);
source.play();
sink.record();
} catch(AlreadyPlayingException e) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,
"Source already playing",
"Play error",
JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
} catch(AlreadyRecordingException e) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,
"Sink already recording",
"Record error",
JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
} catch(Exception e) {
// IncompatableSink/Source
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
System.out.println("Checking VC " + sink);
// printInterfaces(sink.getClass());
if (source instanceof VolumeControl) {
System.out.println("Source is VC");
enableVolumeControl( (VolumeControl) source, sourceVolumeCtl);
}
if (sink instanceof VolumeControl) {
System.out.println("Sink is VC");
enableVolumeControl( (VolumeControl) sink, sinkVolumeCtl);
}
}
/*
private void printInterfaces(Class cls) {
Class[] classes = cls.getInterfaces();
for (int n = 0; n < classes.length; n++) {
System.out.println(classes[n].getName());
}
cls = cls.getSuperclass();
if (cls != null) {
printInterfaces(cls);
}
}
*/
public void notify(RemoteEvent evt) {
Object src = evt.getSource();
System.out.println("Event notified " + src);
System.out.println("Event seq id " + evt.getSequenceNumber());
if ((src instanceof Sink) &&
(evt.getID() == Sink.STOP)) {
System.out.println("Sink stopped event");
ServiceItem[] rest = null;
if (sources != null) {
rest = new ServiceItem[sources.length - 1];
for (int n = 0; n < rest.length; n++) {
rest[n] = sources[n + 1];
}
}
play(rest, sinkItem);
/* The following code is broken, don't know why
It just removes too many off the playlist
Sink sink = (Sink) src;
try {
sink.removeSinkListener((RemoteEventListener) proxy);
System.out.println("Removed listener " + proxy);
} catch(RemoteException e) {
// ignore
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(NoSuchListenerException e) {
System.err.println("Can't remove listener " + proxy);
}
MarshalledObject handback = evt.getRegistrationObject();
SourceSink ss = null;
try {
ss = (SourceSink) handback.get();
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
if (ss == null) {
// no more playlist
return;
}
final ServiceItem[] sources = ss.sources;
final ServiceItem sinkItem = ss.sink;
System.out.println(" stop -> play: sources " + sources + " sink " + sink);
Runnable doPlay = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
play(sources, sinkItem);
}
};
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(doPlay);
*/
} else if ((src instanceof Source) &&
(evt.getID() == Source.STOP)) {
System.out.println("Source stopped event");
}
}
private void enableVolumeControl(VolumeControl vol, JSlider slider) {
int maxVol = 0;
int currVol = 0;
try {
maxVol = vol.getMaxVolume();
if (maxVol <= 0) return;
currVol = vol.getVolume();
System.out.println("Current vol: " + currVol);
if (currVol < 0 || currVol > maxVol) return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
slider.setMinimum(0);
slider.setMaximum(maxVol);
slider.setValue(currVol);
slider.setEnabled(true);
}
/************************************
* Check for UI entries
*/
private void checkUI(ServiceItem item) {
// Find and check the UIDescriptor's
Entry[] attributes = item.attributeSets;
System.out.println("Entries: " + attributes.length);
for (int m = 0; m < attributes.length; m++) {
Entry attr = attributes[m];
System.out.println("Checking Entry " + attr);
if (attr instanceof UIDescriptor) {
System.out.println("Found a UI");
// does it deliver a Swing Dialog?
// how do we decide if we want a Frame or Dialog?
checkForSwingDialog(item, (UIDescriptor) attr);
}
}
}
private void checkForSwingDialog(ServiceItem item, UIDescriptor desc) {
Set attributes = desc.attributes;
Iterator iter = attributes.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
// search through the attributes, to find a UIFactoryTypes
Object obj = iter.next();
if (obj instanceof UIFactoryTypes) {
UIFactoryTypes types = (UIFactoryTypes) obj;
// see if it produces a Swing Dialog Factory
if (types.isAssignableTo(JDialogFactory.class)) {
JDialogFactory factory = null;
try {
factory = (JDialogFactory) desc.getUIFactory(this.getClass().
getClassLoader());
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
continue;
}
System.out.println("calling dialog with " + item);
// how do we decide if it should be modal?
JDialog dialog = factory.getJDialog(item, this, true);
dialog.setVisible(true);
}
}
}
}
}// PlayFrame
A variety of different sources and sinks can be handled by this framework. This is not just different tracks from a CD and different players around the home, but can include different implementations. For example, the equivalent of a cassette recorder can be built by making a sink save its input into a file instead of sending it to the soundcard. This section looks at what is involved in doing this.
If a service is going to save audio to a file, then it will need to allow
a client to specify this file. At the very least, it will need to expose
a setFile method. But it could be more complex than this:
the client may need to browse the service file system before choosing
a name: for example, to record the "Bitches brew" jazz program off PBS-FM
it may want to change to an appropriate directory and check that it isn't
going to overwrite an earlier recording.
File browsing is usually handled in a GUI environment by
JFileChooser. In a non-GUI environment there are methods such
as File.list() to list a directory. However, these are local
methods in local classes: the JFileChooser has no implicit
support for browsing the filesystem of a remote Jini system. But it does
have a hook to allow such remote browsing, through the
FileSystemView class, which is intended to isolate O/S
dependent code into a single class.
Based on the FileSystemView class, we can define an interface
that captures remote file system browsing and choosing a file
/**
* FileSink.java
*/
package audio.filesink;
import java.io.File;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
public interface FileSink extends audio.common.Sink {
public boolean setFile(File sinkFile) throws RemoteException;
/**
* methods to browse the file system
* Based on FileSystemView from JFileChooser
*/
public File[] getFiles(File dir, boolean useFileHiding) throws RemoteException;
public File getHomeDirectory() throws RemoteException;
public File getDefaultDirectory() throws RemoteException;
public File createNewFolder(File dir) throws RemoteException, java.io.IOException;
}// FileSink
While the client sees the interface, the server needs to implement it.
This can be done by keeping a FileSystemView object on
the server side and passing most calls through to it
/**
* SinkImpl.java
*/
package audio.filesink;
import audio.common.*;
import audio.transport.*;
import audio.aumix.*;
import audio.pull.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.rmi.*;
import net.jini.core.event.EventRegistration;
import net.jini.core.event.RemoteEvent;
import java.util.Vector;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import net.jini.core.event.RemoteEventListener;
import net.jini.core.event.UnknownEventException;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import javax.swing.filechooser.FileSystemView;
import common.*;
public class SinkImpl implements FileSink, Remote {
private Source source;
private boolean stopped;
private CopyIO copyIO;
private Hashtable listeners = new Hashtable();
private int seqNum = 0;
private Remote proxy;
private File sinkFile;
private FileSystemView fileView;
public SinkImpl() {
fileView = FileSystemView.getFileSystemView();
}
public void setProxy(Remote proxy) {
this.proxy = proxy;
}
public boolean setFile(File sinkFile) {
this.sinkFile = sinkFile;
System.out.println("File sink set to " + sinkFile);
return true;
}
public void record() throws RemoteException, AlreadyRecordingException {
TransportSink transportSink = null;
InputStream in = null;
if (source == null) {
return;
}
if (source instanceof HttpSource) {
transportSink = new HttpSinkImpl((HttpSource) source);
in = transportSink.getInputStream();
} else if (source instanceof TcpSource) {
System.out.println("Setting up Tcp sink");
transportSink = new TcpSinkImpl((TcpSource) source);
in = transportSink.getInputStream();
System.out.println("Got tcp source input stream " + in);
} else if (source instanceof PullSource) {
in = ((PullSource) source).getInputStream();
} else {
return;
}
if ((copyIO != null) && ( ! stopped)) {
throw new AlreadyRecordingException();
}
stopped = false;
if (in == null) {
System.out.println("Couldn't get input stream");
stopped = true;
return;
}
copyIO = new CopyIO(this, in, source);
copyIO.start();
System.out.println("Play returning");
}
public void stop() throws RemoteException {
stopped = true;
if (copyIO != null) {
copyIO.stopRecord();
}
}
public void contentStopped() {
copyIO = null;
fireNotify(Sink.STOP);
System.out.println("Stopped");
}
public void addSource(Source source) throws
IncompatableSourceException {
//if (Transport.compatable(source, this)) {
this.source = source;
//} else {
//throw new IncompatableSourceException();
//}
}
public void removeSource(Source source) throws
RemoteException,
NoSuchSourceException {
}
public EventRegistration addSinkListener(RemoteEventListener listener,
MarshalledObject handback) {
System.out.println("Adding listener: " + listener);
listeners.put(listener, handback);
return new EventRegistration(0L, proxy, null, 0L);
}
public void removeSinkListener(RemoteEventListener listener) {
listeners.remove(listener);
}
public void fireNotify(int evtType) {
Enumeration elmts = listeners.keys();
System.out.println("Fire notify");
while (elmts.hasMoreElements()) {
RemoteEventListener listener = (RemoteEventListener) elmts.nextElement();
MarshalledObject handback = (MarshalledObject) listeners.get(listener);
RemoteEvent evt = new RemoteEvent(proxy, evtType, seqNum++, handback);
System.out.println("Updating listener " + listener);
try {
listener.notify(evt);
} catch(UnknownEventException e) {
// ??
} catch(RemoteException e) {
// ?
}
}
}
class CopyIO extends Thread {
private SinkImpl sink;
private ContentSink contentSink;
CopyIO(SinkImpl sink, InputStream in, Source source) {
contentSink = ContentSink.createSink(sink, in, source, sinkFile);
this.sink = sink;
}
public void stopRecord() {
if (contentSink != null) {
contentSink.stop();
// stopped = true;
}
}
public void run() {
contentSink.record();
}
}
// For remote file browsing
public File[] getFiles(File dir, boolean useFileHiding) {
return fileView.getFiles(dir, useFileHiding);
}
public File getHomeDirectory() {
return fileView.getHomeDirectory();
}
public File getDefaultDirectory() {
return fileView.getDefaultDirectory();
}
public File createNewFolder(File dir) throws java.io.IOException {
return fileView.createNewFolder(dir);
}
}// SinkImpl
This sink implementation follows the structure of the earlier ones, although
it could be condensed by directly writing to the output file. In this
implementation, this is done by ContentSink writing to the
file instead of to a "play" program:
/**
* ContentSink.java
*/
package audio.filesink;
import java.io.*;
import audio.presentation.*;
import audio.common.*;
public class ContentSink {
private InputStream in;
private OutputStream out;
private boolean stopped = false;
private SinkImpl sink;
private File outFile;
public static ContentSink createSink(SinkImpl sink,
InputStream in, Source source,
File outFile) {
ContentSink csink = new ContentSink(sink, in, outFile);
return csink;
}
private ContentSink(SinkImpl sink, InputStream in, File outFile) {
this.sink = sink;
this.in = in;
this.outFile = outFile;
System.out.println("Content sink set to " + outFile);
}
public void record() {
InputStream err = null;
try {
out = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(outFile));
} catch(IOException e) {
System.err.println("Playing " + e.toString());
// ignore
return;
}
int ch;
try {
while (((ch = in.read()) != -1) &&
(! stopped)) {
out.write(ch);
}
} catch(IOException e) {
// ignore
System.err.println("Exception writing " + e.toString());
int navail = 0;
try {
if ((navail = err.available()) > 0 ) {
byte avail[] = new byte[navail];
int nread = err.read(avail, 0, navail);
System.out.println("Error channel " +
new String(avail));
}
} catch(IOException ee) {
ee.printStackTrace();
}
return;
} finally {
if (stopped) {
System.out.println("Record stop called");
} else {
System.out.println("Record finished naturally");
stopped = true;
}
try {
in.close();
out.close();
} catch(IOException e) {
// ignore
System.out.println("Finally " + e);
}
sink.contentStopped();
}
}
public void stop() {
if (stopped) {
return;
}
stopped = true;
}
}// ContentSink
The classes listed above are sufficient for a non-GUI client to interact with a file sink by making remote method calls on it. This could be suitable for an automated recording system ("record this show each week") where a client starts to record to the service at a given time each week and stops the record once the time is up.
If the client is a GUI client, then it may want to allow the user to
browse the remote file system using a JFileChooser.
This can be done using the UI packages recently approved for Jini
which are discussed in their own chapter. Here we just use them.
The JFileChooser has a FileSystemViewer object.
This encapsulates many operating specific methods, such as
File[] getFiles() and File createNewFolder().
The JFileChooser will run in a client, but we want it to
be able to access a remote file system where it will save files.
The FileSink discussed in the last section can almost be
used for this, except it is a remote object and all of its methods
throw RemoteException. So we have to wrap it in an object
that will catch all these exceptions and return suitable values.
For want of any better idea, we return null, although
possibly a warning dialog should be popped up first.
/**
* RemoteFileSystemViewWrapper.java
*/
package audio.filesink;
import javax.swing.filechooser.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
public class RemoteFileSystemViewWrapper extends FileSystemView {
private FileSink sink;
public RemoteFileSystemViewWrapper(FileSink sink) {
this.sink = sink;
}
public File createNewFolder(File dir) throws IOException {
try {
return sink.createNewFolder(dir);
} catch(RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
public File[] getFiles(File dir, boolean useFileHiding) {
try {
return sink.getFiles(dir, useFileHiding);
} catch(RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
public File getDefaultDirectory() {
try {
return sink.getDefaultDirectory();
} catch(RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
public File getHomeDirectory() {
try {
return sink.getHomeDirectory();
} catch(RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}
The exported service will be a proxy for a SinkImpl which
implements the FileSink interface. The client will want to
run a dialog which pops up a JFileChooser with a
FileSystemViewer set to a RemoteFileSystemViewerWrapper
which wraps around the FileSink service. When a selection is made,
it can set the file in the service.
/**
* FileSinkJDialog.java
*/
package audio.filesink;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import net.jini.lookup.ui.MainUI;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceItem;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import javax.swing.filechooser.FileSystemView;
public class FileSinkJDialog extends JDialog implements MainUI, ActionListener {
private JFileChooser chooser;
private FileSink sink;
public FileSinkJDialog(Frame owner, ServiceItem item,
String name, boolean modal) {
super(owner, name, modal);
sink = (FileSink) item.service;
// setup a filter based on sink.getSource() ifaces
// ...
RemoteFileSystemViewWrapper fileView = new RemoteFileSystemViewWrapper(sink);
chooser = new JFileChooser((FileSystemView) fileView);
chooser.addActionListener(this);
getContentPane().add(chooser, BorderLayout.CENTER);
pack();
}
public FileSinkJDialog(Dialog owner, ServiceItem item,
String name, boolean modal) {
super(owner, name, modal);
sink = (FileSink) item.service;
// setup a filter based on sink.getSource() ifaces
// e.g. to only show .wav or .ogg files
// ... not done yet
RemoteFileSystemViewWrapper fileView = new RemoteFileSystemViewWrapper(sink);
chooser = new JFileChooser((FileSystemView) fileView);
chooser.addActionListener(this);
getContentPane().add(chooser, BorderLayout.CENTER);
pack();
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (e.getActionCommand().equals(JFileChooser.APPROVE_SELECTION)) {
// file selected
System.out.println("Selected file: " + chooser.getSelectedFile());
try {
sink.setFile(chooser.getSelectedFile());
setVisible(false);
} catch(RemoteException re) {
System.out.println("" + re);
}
} else {
System.out.println("Other event: " + e);
}
}
}// FileSinkJDialog
As discussed in the chapter on user interfaces, it is not possible to just
send a FileSinkJDialog to a client, because it may not have the
classes or memory to handle such an object. The first stage in hiding this
is to use a factory object to produce it. This factory follows exactly
the pattern for this factory, just changing the returned object to a
FileSinkJDialog
/**
* FileSinkJDialogFactory.java
*/
package audio.filesink;
import net.jini.lookup.ui.factory.JDialogFactory;
import net.jini.lookup.entry.UIDescriptor;
import javax.swing.JDialog;
import net.jini.core.entry.Entry;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceItem;
import java.awt.*;
public class FileSinkJDialogFactory implements JDialogFactory {
/**
* Return a new FileSinkJDialog that implements the
* MainUI role
*/
public JDialog getJDialog(Object roleObject, Frame owner, boolean modal) {
// we should check to see what role we have to return
if (! (roleObject instanceof ServiceItem)) {
// unkown role type object
// can we return null?
return null;
}
ServiceItem item = (ServiceItem) roleObject;
// Do sanity checking that the UIDescriptor has a MainUI role
Entry[] entries = item.attributeSets;
for (int n = 0; n < entries.length; n++) {
if (entries[n] instanceof UIDescriptor) {
UIDescriptor desc = (UIDescriptor) entries[n];
if (desc.role.equals(net.jini.lookup.ui.MainUI.ROLE)) {
// Ok, we are in the MainUI role, so return a UI for that
JDialog dialog = new FileSinkJDialog(owner, item,
"File sink", modal);
return dialog;
}
}
}
// couldn't find a role the factory can create
return null;
}
public JDialog getJDialog(Object roleObject) {
return getJDialog(roleObject, (Frame) null, false);
}
public JDialog getJDialog(Object roleObject, Dialog owner) {
return getJDialog(roleObject, owner, false);
}
public JDialog getJDialog(Object roleObject, Dialog owner,
boolean modal) {
// we should check to see what role we have to return
if (! (roleObject instanceof ServiceItem)) {
// unkown role type object
// can we return null?
return null;
}
ServiceItem item = (ServiceItem) roleObject;
// Do sanity checking that the UIDescriptor has a MainUI role
Entry[] entries = item.attributeSets;
for (int n = 0; n < entries.length; n++) {
if (entries[n] instanceof UIDescriptor) {
UIDescriptor desc = (UIDescriptor) entries[n];
if (desc.role.equals(net.jini.lookup.ui.MainUI.ROLE)) {
// Ok, we are in the MainUI role, so return a UI for that
JDialog dialog = new FileSinkJDialog(owner, item,
"File sink", modal);
return dialog;
}
}
}
// couldn't find a role the factory can create
return null;
}
public JDialog getJDialog(Object roleObject, Frame owner) {
return getJDialog(roleObject, owner, false);
}
}// FileSinkJDialogFactory
Finally from the server side, the factory has to marshalled (to hide its classes)
and embedded into a UIDescriptor entry object as part of the
service advertisement. This is accomplished by the getEntry()
method, which is called in preparing the Entry[] array
package audio.filesink;
import net.jini.lookup.JoinManager;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceID;
import net.jini.discovery.LookupDiscovery;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceRegistrar;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import net.jini.lookup.ServiceIDListener;
import net.jini.lease.LeaseRenewalManager;
import net.jini.discovery.LookupDiscoveryManager;
import net.jini.discovery.DiscoveryEvent;
import net.jini.discovery.DiscoveryListener;
import java.rmi.RMISecurityManager;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import net.jini.config.*;
import net.jini.export.*;
import net.jini.id.UuidFactory;
import net.jini.id.Uuid;
import net.jini.core.entry.Entry;
import net.jini.lookup.entry.*;
import net.jini.lookup.ui.MainUI;
import java.rmi.MarshalledObject;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.HashSet;
import net.jini.lookup.ui.factory.JDialogFactory;
import net.jini.lookup.ui.attribute.UIFactoryTypes;
import java.io.*;
/**
* SinkServer.java
*/
public class SinkServer
implements ServiceIDListener {
// explicit proxy for Jini 2.0
protected Remote proxy;
protected SinkImpl impl;
private String sinkName = "No name";
private ServiceID serviceID;
public static void main(String argv[]) {
new SinkServer(argv);
// stay around forever
Object keepAlive = new Object();
synchronized(keepAlive) {
try {
keepAlive.wait();
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
// do nothing
}
}
}
public SinkServer(String[] argv) {
File serviceIDFile = null;
try {
impl = new SinkImpl();
} catch(Exception e) {
System.err.println("New impl: " + e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
try {
// get the configuration (by default a FileConfiguration)
Configuration config = ConfigurationProvider.getInstance(argv);
// and use this to construct an exporter
Exporter exporter = (Exporter) config.getEntry( "FileSinkServer",
"exporter",
Exporter.class);
// export an object of this class
proxy = exporter.export(impl);
impl.setProxy(proxy);
sinkName = (String) config.getEntry( "FileSinkServer",
"sinkName",
String.class);
serviceIDFile = (File) config.getEntry("FileSinkServer",
"serviceIdFile",
File.class);
getOrMakeServiceID(serviceIDFile);
} catch(Exception e) {
System.err.println(e.toString());
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
// install suitable security manager
System.setSecurityManager(new RMISecurityManager());
JoinManager joinMgr = null;
try {
LookupDiscoveryManager mgr =
new LookupDiscoveryManager(LookupDiscovery.ALL_GROUPS,
null, // unicast locators
null); // DiscoveryListener
joinMgr = new JoinManager(proxy, // service proxy
new Entry[] {new Name(sinkName),
getUIEntry()}, // attr sets
serviceID, // ServiceID
mgr, // DiscoveryManager
new LeaseRenewalManager());
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
private Entry getUIEntry() {
// The typenames for the factory
Set typeNames = new HashSet();
typeNames.add(JDialogFactory.TYPE_NAME);
// The attributes set
Set attribs = new HashSet();
attribs.add(new UIFactoryTypes(typeNames));
// The factory
MarshalledObject factory = null;
try {
factory = new MarshalledObject(new FileSinkJDialogFactory());
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(2);
}
UIDescriptor desc = new UIDescriptor(MainUI.ROLE,
JDialogFactory.TOOLKIT,
attribs,
factory);
return desc;
}
private void getOrMakeServiceID(File serviceIDFile) {
try {
ObjectInputStream ois =
new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(serviceIDFile));
serviceID = (ServiceID) ois.readObject();
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("Couldn't get service IDs - generating new ones");
try {
ObjectOutputStream oos =
new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(serviceIDFile));
Uuid uuid = UuidFactory.generate();
serviceID = new ServiceID(uuid.getMostSignificantBits(),
uuid.getLeastSignificantBits());
oos.writeObject(serviceID);
} catch(Exception e2) {
System.out.println("Couldn't save ids");
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void serviceIDNotify(ServiceID serviceID) {
// called as a ServiceIDListener
// Should save the id to permanent storage
System.out.println("got service ID " + serviceID.toString());
}
} // SinkServer
Finally, the client has to be modified to look for UI objects and to use them
as part of the user interaction. The client is the same as the GUI client
discussed earlier except that in the PlayFrame object it checks
for a UIDescriptor
/**
* PlayFrame.java
*/
package audio.client;
import audio.common.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import net.jini.core.event.RemoteEvent;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import net.jini.core.event.RemoteEventListener;
import java.rmi.MarshalledObject;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import javax.swing.event.*;
import net.jini.core.entry.Entry;
import net.jini.lookup.ui.MainUI;
import net.jini.lookup.ui.factory.JDialogFactory;
import net.jini.lookup.entry.UIDescriptor;
import net.jini.lookup.ui.attribute.UIFactoryTypes;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.Iterator;
import net.jini.core.lookup.ServiceItem;
/**
* Play a selection of sources to a single sink
*/
public class PlayFrame extends JFrame implements ActionListener,
ChangeListener,
RemoteEventListener {
private ServiceItem[] sources;
private ServiceItem sinkItem;
private Sink sink;
private Source source;
private boolean firstTime = true;
private JList sourceList = new JList();
private JButton stopBtn = new JButton("Stop");
private JButton stopAllBtn = new JButton("Stop all");
private JLabel sinkLabel = new JLabel();
private JSlider sourceVolumeCtl = new JSlider();
private JSlider sinkVolumeCtl = new JSlider();
private DefaultListModel model;
private Remote proxy;
private GUIClient client;
public PlayFrame(GUIClient client) {
setTitle("Player");
this.client = client;
JPanel bottomPanel = new JPanel();
bottomPanel.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
Container contentPane = getContentPane();
contentPane.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
contentPane.add(sinkLabel, BorderLayout.NORTH);
contentPane.add(sourceList, BorderLayout.CENTER);
contentPane.add(bottomPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
JPanel volumeControls = new JPanel();
volumeControls.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 2));
volumeControls.add(sourceVolumeCtl);
volumeControls.add(sinkVolumeCtl);
JPanel buttons = new JPanel();
buttons.setLayout(new GridLayout(1,3));
buttons.add(stopBtn);
buttons.add(stopAllBtn);
bottomPanel.add(volumeControls, BorderLayout.NORTH);
bottomPanel.add(buttons, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
stopBtn.addActionListener(this);
stopAllBtn.addActionListener(this);
LabelCellRenderer labelRend = new LabelCellRenderer();
sourceList.setCellRenderer(labelRend);
model = new DefaultListModel();
sourceList.setModel(model);
sourceVolumeCtl.setEnabled(false);
sinkVolumeCtl.setEnabled(false);
sourceVolumeCtl.addChangeListener(this);
sinkVolumeCtl.addChangeListener(this);
sourceVolumeCtl.setToolTipText("Set volume on the source");
sinkVolumeCtl.setToolTipText("Set volume on the sink");
setSize(400, 300);
setVisible(true);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) {
if (evt.getSource() == stopBtn) {
try {
sink.stop();
sinkVolumeCtl.setEnabled(false);
sourceVolumeCtl.setEnabled(false);
} catch(RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(NotRecordingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else if (evt.getSource() == stopAllBtn) {
/* This doesn;t work right
// kill the rest of the playlist by removing
// our listener and putting in a new one with
// null playback
try {
sink.removeSinkListener((RemoteEventListener) proxy);
System.out.println("Removed listener " + proxy);
sink.addSinkListener((RemoteEventListener) proxy,
new MarshalledObject(
new SourceSink(null, null)));
System.out.println("Added listener with null playback");
} catch(RemoteException e) {
// ignore
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(NoSuchListenerException e) {
System.err.println("Can't change listener " + proxy);
} catch(IOException e) {
System.err.println("Can't marshall null " + proxy);
}
*/
// to fix above... when the stop event arrives, we will try to play but just terminate
sources = null;
// now stop the play
try {
sink.stop();
sinkVolumeCtl.setEnabled(false);
sourceVolumeCtl.setEnabled(false);
} catch(RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(NotRecordingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void stateChanged(ChangeEvent e) {
JSlider slider = (JSlider) e.getSource();
int vol = slider.getValue();
VolumeControl volCtl = null;
if (slider == sinkVolumeCtl) {
volCtl = (VolumeControl) sink;
} else if (slider == sourceVolumeCtl) {
volCtl = (VolumeControl) source;
}
try {
volCtl.setVolume(vol);
} catch(RemoteException ex) {
// ignore
}
}
public void play(ServiceItem[] sources, ServiceItem sinkItem) {
if ((sources == null) || (sources.length == 0)) {
System.out.println("Play: null sources");
// dispose();
Runnable doDispose = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
dispose();
}
};
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(doDispose);
return;
}
this.sources = sources;
this.sinkItem = sinkItem;
sink = (Sink) sinkItem.service;
source = (Source) sources[0].service;
sinkLabel.setText("Playing to " + sinkItem.toString());
model.clear();
for (int n = 0; n < sources.length; n++) {
model.addElement(sources[n]);
}
// just give the event source something it can put in a table
MarshalledObject handback = null;
try {
handback = new MarshalledObject(null);
} catch(java.io.IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
/*
ServiceItem[] rest = new ServiceItem[sources.length - 1];
for (int n = 0; n < rest.length; n++) {
rest[n] = sources[n + 1];
}
MarshalledObject handback = null;
try {
handback = new MarshalledObject(new SourceSink(rest, sinkItem));
} catch(java.io.IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
*/
try {
// this is a bit of a hack
if (firstTime) {
if (proxy == null) {
proxy = client.export(this);
}
// source.addSourceListener((RemoteEventListener) proxy, null);
System.out.println("Added source " + source + " proxy " + proxy);
sink.addSinkListener((RemoteEventListener) proxy, handback);
System.out.println("Added sink " + sink + " proxy " + proxy + " handback " +
"null" /*((SourceSink) handback.get()).sources*/ );
firstTime = false;
}
} catch(RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try{
System.out.println("Setting sink to: " + sink);
source.addSink(sink);
System.out.println("Setting source to: " + source);
sink.addSource(source);
System.out.println("Playing" + sources[0].attributeSets[0]);
// check for UI elements
checkUI(sinkItem);
source.play();
sink.record();
} catch(AlreadyPlayingException e) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,
"Source already playing",
"Play error",
JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
} catch(AlreadyRecordingException e) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,
"Sink already recording",
"Record error",
JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
} catch(Exception e) {
// IncompatableSink/Source
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
System.out.println("Checking VC " + sink);
// printInterfaces(sink.getClass());
if (source instanceof VolumeControl) {
System.out.println("Source is VC");
enableVolumeControl( (VolumeControl) source, sourceVolumeCtl);
}
if (sink instanceof VolumeControl) {
System.out.println("Sink is VC");
enableVolumeControl( (VolumeControl) sink, sinkVolumeCtl);
}
}
/*
private void printInterfaces(Class cls) {
Class[] classes = cls.getInterfaces();
for (int n = 0; n < classes.length; n++) {
System.out.println(classes[n].getName());
}
cls = cls.getSuperclass();
if (cls != null) {
printInterfaces(cls);
}
}
*/
public void notify(RemoteEvent evt) {
Object src = evt.getSource();
System.out.println("Event notified " + src);
System.out.println("Event seq id " + evt.getSequenceNumber());
if ((src instanceof Sink) &&
(evt.getID() == Sink.STOP)) {
System.out.println("Sink stopped event");
ServiceItem[] rest = null;
if (sources != null) {
rest = new ServiceItem[sources.length - 1];
for (int n = 0; n < rest.length; n++) {
rest[n] = sources[n + 1];
}
}
play(rest, sinkItem);
/* The following code is broken, don't know why
It just removes too many off the playlist
Sink sink = (Sink) src;
try {
sink.removeSinkListener((RemoteEventListener) proxy);
System.out.println("Removed listener " + proxy);
} catch(RemoteException e) {
// ignore
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(NoSuchListenerException e) {
System.err.println("Can't remove listener " + proxy);
}
MarshalledObject handback = evt.getRegistrationObject();
SourceSink ss = null;
try {
ss = (SourceSink) handback.get();
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
if (ss == null) {
// no more playlist
return;
}
final ServiceItem[] sources = ss.sources;
final ServiceItem sinkItem = ss.sink;
System.out.println(" stop -> play: sources " + sources + " sink " + sink);
Runnable doPlay = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
play(sources, sinkItem);
}
};
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(doPlay);
*/
} else if ((src instanceof Source) &&
(evt.getID() == Source.STOP)) {
System.out.println("Source stopped event");
}
}
private void enableVolumeControl(VolumeControl vol, JSlider slider) {
int maxVol = 0;
int currVol = 0;
try {
maxVol = vol.getMaxVolume();
if (maxVol <= 0) return;
currVol = vol.getVolume();
System.out.println("Current vol: " + currVol);
if (currVol < 0 || currVol > maxVol) return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
slider.setMinimum(0);
slider.setMaximum(maxVol);
slider.setValue(currVol);
slider.setEnabled(true);
}
/************************************
* Check for UI entries
*/
private void checkUI(ServiceItem item) {
// Find and check the UIDescriptor's
Entry[] attributes = item.attributeSets;
System.out.println("Entries: " + attributes.length);
for (int m = 0; m < attributes.length; m++) {
Entry attr = attributes[m];
System.out.println("Checking Entry " + attr);
if (attr instanceof UIDescriptor) {
System.out.println("Found a UI");
// does it deliver a Swing Dialog?
// how do we decide if we want a Frame or Dialog?
checkForSwingDialog(item, (UIDescriptor) attr);
}
}
}
private void checkForSwingDialog(ServiceItem item, UIDescriptor desc) {
Set attributes = desc.attributes;
Iterator iter = attributes.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
// search through the attributes, to find a UIFactoryTypes
Object obj = iter.next();
if (obj instanceof UIFactoryTypes) {
UIFactoryTypes types = (UIFactoryTypes) obj;
// see if it produces a Swing Dialog Factory
if (types.isAssignableTo(JDialogFactory.class)) {
JDialogFactory factory = null;
try {
factory = (JDialogFactory) desc.getUIFactory(this.getClass().
getClassLoader());
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
continue;
}
System.out.println("calling dialog with " + item);
// how do we decide if it should be modal?
JDialog dialog = factory.getJDialog(item, this, true);
dialog.setVisible(true);
}
}
}
}
}// PlayFrame
This chapter has discussed a framework for distributed audio. Jini makes it fairly straightforward to handle service advertisement and discovery, telling services about each other and generatikng and handling remote events. The architecture is extensible just be adding in more interfaces and implementations. For example, I am currently adding a "file sink" so that I can record audio to file. If this is linked to an FM tuner card then I will be able to record my favourite shows from a timer program.
If you found this chapter of value, the full book "Foundations of Jini 2 Programming" is available from APress or Amazon .
 This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons License, the replacement for the earlier Open Content License.
This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons License, the replacement for the earlier Open Content License.