This chapter looks at some of the problems that can arise in a Jini system. Most of them are configuration problems of some kind. This chapter is woefully incomplete :-((( Contributions welcome!!!
Jini is advertised as ``network plug and play''. This carries the idea of ``zero administration'' where you buy a device, switch it on and voila it is there and available. Well, this may happen in the future, but right now there are a number of back-room games that you have to succeed at. Once you have won at these, ``network plug and play'' does work, but if you lose at any stage then it can be all uphill!
What is hard is issues of getting the right files in the right places with the right permissions. About 50% of the messages in the Jini mailing list are all about these configuration problems. These shouldn't occur, and that is why this is ``The Chapter that Shouldn't Exist''.
This is the second chapter in this book, so right now you shouldn't have managed to fail at anything! Each of the early sections contains instructions on what to do to get the example programs working, and include step-by-step instructions. So skip on to the next chapters, but come back here when things go wrong. Your luck may vary: I got quite a reasonable way on my first attempts without problems, and some are even luckier. Some aren't...
Typical error:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError:
basic/InvalidLookupLocator
Most of the code in this tutorial is organised into packages. To run
the examples the classes must be accessible from your class path. For
example, one of the programs in the basic directory is
InvalidLookupLocator.java. This defines the class
InvalidLookupLocator in the package basic.
The program must be run using the fully qualified path name, as in
java basic.InvalidLookupLocator
In order to find this class, the classpath must be set correctly for
the Java runtime. If you have copied the zip file classes.zip
then the class files for this tutorial are in there. You only need to
reference this
CLASSPATH=classes.zip:...
If you have downloaded the source files, then they are all in subdirectories
such as basic, complex, etc. After compilation the
class files should also be in these subdirectories, such as
basic/InvalidLookupLocator.class. An alternative to using
classes.zip is to set the classpath to include the
directory containing those subdirectories. For example, if the full path
is say /home/jan/classes/basic/InvalidLookupLocator.class,
then set classpath to
CLASSPATH=/home/jan/classes:...
An alternative to setting the CLASSPATH environment variable
is to use the -classpath option to the Java runtime engine
java -classpath /home/jan/classes basic.InvalidLookupLocator
There are four versions of Jini: 1.0, 1.1, 1.2 and the new 2.0. The core classes are all the same. This version of the book will only deal with the new 2.0. Jini 2.0 requires JDK 1.4 or later, not earlier versions of Java.
The changes for 2.0 are listed in the document "jini2_0/doc/release-notes/new.html"
Typical error
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError:
net/jini/discovery/DiscoveryListener
The Jini class files are all in jar files.
The Jini distribution has them in a subdirectory lib
when it is unpacked.
There are a whole bunch of these jar files:
jini-core.jar mahalo-dl.jar sun-util.jar
jini-examples-dl.jar mahalo.jar tools.jar
jini-examples.jar reggie-dl.jar
jini-ext.jar reggie.jar
The jar file jini-core.jar contains the major packages of Jini
net.jini.core
net.jini.core.discovery
net.jini.core.entry
net.jini.core.event
net.jini.core.lease
net.jini.core.lookup
net.jini.core.transaction
jini-core.jar is in your classpath.
The jar file jini-ext.jar contains a set of packages
which are not in the core, but are still heavily used
net.jini.admin
net.jini.discovery
net.jini.entry
net.jini.lease
net.jini.lookup
net.jini.lookup.entry
net.jini.space
jini-ext.jar is in your classpath.
The jar file sun-util.jar contains the packages
from the com.sun.jini hierarchy.
These contain a number of ``convenience'' classes that are
not essential but can be useful. These are less frequently
used.
A compile or run of a Jini application will typically have an environment set something like
JINI_HOME=wherever_Jini_home_is
CLASSPATH=.:$JINI_HOME/lib/jini-core.jar:$JINI_HOME/lib/jini-ext.jar
java.rmi.ServerException: RemoteException in server thread; nested exception is:
java.rmi.UnmarshalException: unmarshalling method/arguments; nested exception is:
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: could not obtain preferred value for: ...
java.rmi.server.codebase is pointing to. Note that using
localhost is a common error since it may refer to a different
machine to the intended one.
A long-term aim in pervasive computing is to have zero configuration, whereby you can plug devices into a network and things "just work". Jini goes a long way towards making this possible at the service level, but the current implementation relies heavily on a functioning network layer: problems with misconfiguration of the network can cause lots of problems to Jini.
Typical error
java.rmi.ConnectException: connection refused or timed out to
BasicObjectEndpoint[88133900-39f9-466a-880b-de8ce6653a63,
TcpEndpoint[0.0.0.0:1831]]; nested exception is:
java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused
exporter = new BasicJeriExporter(TcpServerEndpoint.getInstance(0),
new BasicILFactory());
InetAddress.getLocalHost()) was
unable to determine the IP address of localhost and returned "0.0.0.0" -
and nothing could connect to that address!
The solution was to correctly set the hostname on that machine. Then services could
be found and run on that machine. Alternatively, TcpServerEndpoint.getInstance(0)
could be replaced by TcpServerEndpoint.getInstance("my_ip_address", 0)
(for a suitable "my_ip_address" of course!) in the configuration files for the
services in that machine.
Jini can't find a class file. Something is wrong with the classpath or the codebase. This can occur if the codebase points to a directory, and the value is not terminated with a "/"
Typical error
java.rmi.activation.ActivationException: ActivationSystem not running;
nested exception is:
java.rmi.NotBoundException: java.rmi.activation.ActivationSystem
java.rmi.NotBoundException: java.rmi.activation.ActivationSystem
rmid starts the ``activation system'' running.
If this cannot start properly or dies just after starting, you will get
this message. Usually it is caused by incorrect file permissions.
Typical error
java.rmi.StubNotFoundException:
Stub class not found: rmi.FileClassifierImpl_Stub;
nested exception is:
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: rmi.FileClassifierImpl_Stub
Many of the examples export services as remote RMI objects.
These objects are subclasses of UnicastRemoteObject.
What gets exported is not the object itself, but a stub
that will act as proxy for the object (which continues to run back
in the server). The stub has to be created using the rmic
compiler as in
rmic -v1.2 -d . rmi.FileClassifierImpl
FileClassifierImpl_Stub.class in the
rmi subdirectory. The stub class file needs to be accessible
to the Java runtime in the same way as the original class file.
Another typical error is
java.rmi.ServerException: RemoteException occurred in server thread; nested exception is:
java.rmi.UnmarshalException: error unmarshalling arguments; nested exception is:
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: rmi.FileClassifierImpl_Stub
FileClassifierImpl, and it is trying to load the class file for the
stub from an HTTP server.
What makes this one particularly annoying is that it may not be referring
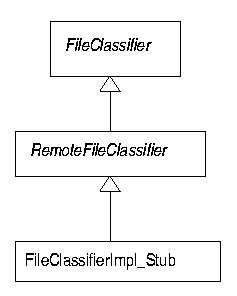
to the FileClassifierImpl_Stub at all! The class will often implement
a remote interface such as RemoteFileClassifier. This in turn implements
the common class FileClassifier as in Figure 2.1.

FileClassifier may be ``well known'', with a class
file on each client and server. However, an interface such as
RemoteFileClassifier as well as the implementation files for
FileClassifierImpl may only be known to a particular server.
The HTTP server must carry not only the
class files for the stubs, but the class files for all superclasses and interfaces
that are not available to all - in this case, for RemoteFileClassifier
as well as FileClassfier.
Typical error
java.rmi.ConnectException: connection refused or timed out to BasicObjectEndpoint[afeb7958-8cff-41cb-8042-ec884a52e9a6,TcpEndpoint[192.168.2.1:3558]]; nested exception is:
java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused
The solution is to ensure that an active reference is kept to the service.
The main() method should contain a reference to the server
(not just create it, but also keep a variable pointing to it).
The server should also keep a reference to the service implementation.
An alternative is to keep a static reference to the service implementation.
Similarly, if you are using a JoinManager to keep services
leased then there should be an active reference to it or it may be garbage
collected and cause any leases to expire.
Debugging a Jini application is difficult because there are so many bits to it, and these bits are all running separately: the server for a service, the client, lookup services, remote activation daemons and HTTP servers. There are a few (not many) errors within the Jini objects themselves, but more importantly many of these objects are implemented using multiple threads and the flow of execution is not always clear. There are no magic ``debug'' flags that can be turned on to show what is happening.
On either the client or service side, a debugger such as jdb
can be used to step through or trace execution of each one. Lots of
print statements help too. There are also three flags that can be turned
on to help:
java -Djava.security.debug=access \
-Dnet.jini.discovery.debug=1 \
-Djava.rmi.server.logCalls=true ...
The logging APIU can also be used for debugging, and is considered in a later chapter.
The logging API introduced in Jini 1.4 has been adopted by Jini 2.0. This can also be used for debugging, and is discussed in its own chapter.
If you found this chapter of value, the full book is available from APress or Amazon . There is a review of the book at Java Zone . The current edition of the book does not yet deal with Jini 2.0, but the next edition will.
 This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons License, the replacement for the earlier Open Content License.
This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons License, the replacement for the earlier Open Content License.