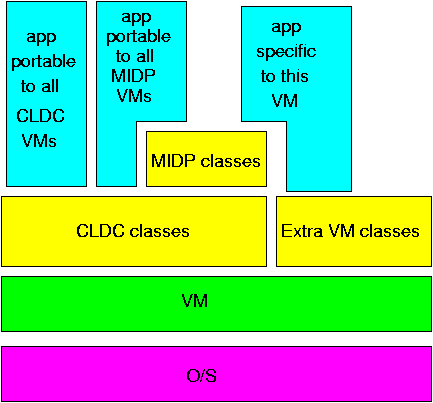

Connector class to open communication with
something else
Connection conn = Connector.open("...");
open() method takes a string that defines
the connection type
Connector.open("http://www.monash.edu.au")
Connector.open("socket://www.monash.edu.au:80")
Connector.open("comm:0;baudrate=9600")
Connector.open("datagram:www.monash.edu.au:10")
Connector.open("file:/etc/passwd")
open() will throw a
ConnectionNotFoundException if the connection type
is not supported
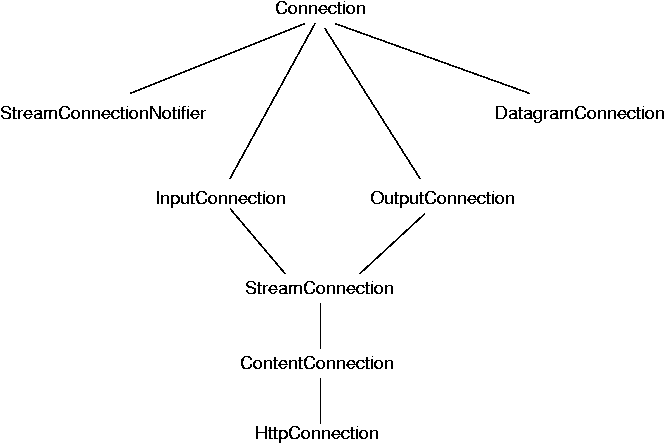
InputConnection, and the input
stream can be found by
InputStream in = (InputConnection) conn.getInputStream();
DataInputStream din = (DataInputStream) conn.getDataInputStream();
InputStream in = null;
if (conn instanceof InputConnection) {
in = (InputConnection) conn.getInputStream();
...
} else {...}
OutputConnection is for writing,
StreamConnection for both,
DatagramConnection for UDP packets
ContentConnection is where the stream conveys a
particular type of data, such as a GIF image sent by HTTP
StreamConnectionNotifier can be used if the
device can be a server, such as a Web server: it has to
wait for connections to come in
HttpConnection
HttpConnection conn = (HttpConnection)
Connector.open("http://www.monash.edu.au);
HttpConnection class is similar to the
java.net.URLConnection class in J2SE
void getFromHttpConnection(String url) throws IOException {
HttpConnection conn = null;
InputStream is = null;
try {
conn = (HttpConnection )Connector.open(url);
// Getting the InputStream will open the connection
// and read the HTTP headers. They are stored until
// requested.
is = conn.openInputStream();
// Get the ContentType
String type = conn.getType();
// Get the length and process the data
int len = (int) conn.getLength();
if (len > 0) {
byte[] data = new byte[len];
int actual = is.read(data);
...
} else {
int ch;
while ((ch = is.read()) != -1) {
...
}
}
} finally {
if (is != null)
is.close();
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
}
}
HttpConnection conn = (HttpConnection)
Connector.open("http://www.monash.edu.au?x=abcd");
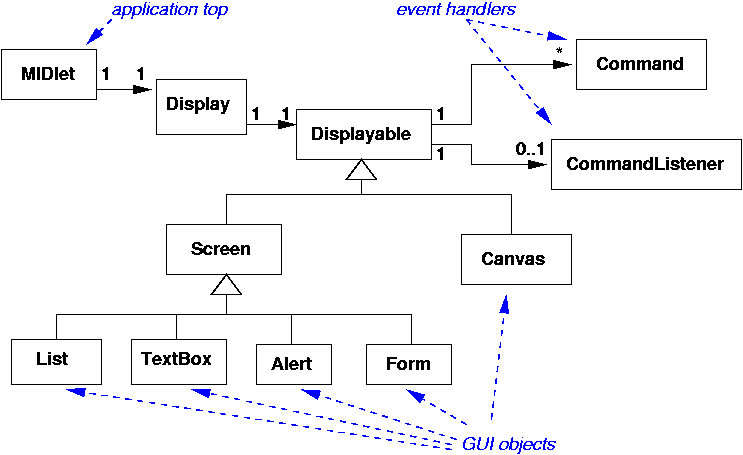
MIDlet
MIDlet.startApp()
public class MyApp extends MIDlet {
public void startApp() {
// we get going here
}
public void pauseApp() {
// we aren't showing any more
}
public void destroyApp(boolean unconditional) {
// clean up
}
}
Assume you have unpacked the J2ME wireless toolkit into a directory such as
WTK=/usr/local/personaljava/WTK2.0
javac -bootclasspath $WTK/lib/midpapi20.zip Shell.java
$WTK/bin/preverify -classpath .:$WTK/lib/midpapi20.zip -d classes Shell
$WTK/bin/emulator -cp classes:$WTK/lib/midpapi20.zip Shell
-Xdevice:device
option, where device is one of
DefaultColorPhone,
DefaultGrayPhone,
MediaControlSkin or
QwertyDevice
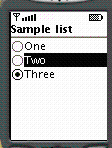
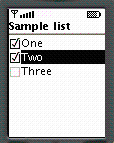
Command class places "buttons" on the screen
to interact with the application, such as an "Okay" button
BACK, CANCEL, HELP,
EXIT, ITEM, OK,
SCREEN and STOP
ITEM command refers to a particular item
on the screen, such as a part of a form
SCREEN command means some application-specific
action based on the current screen, such as "ring the user now"
Command comm = new Command("Ok", Command.OK, 1)
Displayable objects like
List
List)
so that the application can respond to events to that occur in
commands attached to the displayable
CommandListener interface, and implement the method
public void commandAction(Command c, Displayable d)
TextBox gives a full-screen (!) text editor
Form is the only "container" class in MIDP
Form can contain Item objects
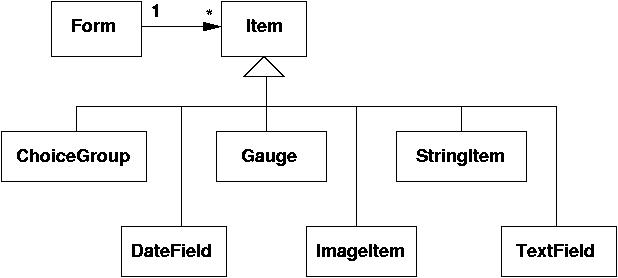
Form.append()
form.append(item);
form.append("string");
ItemStateChanged event
ItemStateListener
which is set on the form
ItemStateListener method
public void itemStateChanged(Item item)
Canvas
public void repaint(); // call this to redraw the screen
public void paint(Graphics g); // override this to draw your things
Graphics object has methods to draw lines, text, etc
public class Graphics {
void drawChar(char character, int x, int y, int anchor);
void drawLine(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2);
void drawRect(int x, int y, int width, int height);
void fillArc(int x, int y, int width, int height,
int startAngle, int arcAngle);
void fillRect(int x, int y, int width, int height);
void setColor(int red, int green, int blue);
void setFont(Font font);
// etc
}
public class Canvas {
void keyPressed(int keyCode);
void keyReleased(int keyCode);
void keyRepeated(int keyCode);
void showNotify();
void hideNotify();
void pointerDragged(int x, int y);
// etc
}
char
Graphics
method
String getKeyName(int keycode)
int getGameAction(int keycode)
translates keycodes to game actions
RecordStore to store records of binary data
RecordStore
ObjectOutputStream (and input equivalent)
to serialize a class
RecordStore.openRecordStore(String name, boolean createIfNeeded)
RecordStore.deleteRecordStore(String recordStoreName)
RecordStoreException
public int addRecord(byte[] data,
int offset,
int numBytes)
throws RecordStoreNotOpenException,
RecordStoreException,
RecordStoreFullException
RecordEnumeration enumerateRecords(RecordFilter filter,
RecordComparator comparator,
boolean keepUpdated)
RecordEnumeration has methods including
boolean hasNextElement();
byte[] nextRecord();