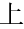
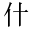
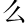 consisting of a one-character word and a two-character word.
consisting of a one-character word and a two-character word.
| Not followed by canonical composition | Followed by canonical composition | |
|---|---|---|
| Canonical decomposition |
|
|
| Compatable decomposition |
|
|
sun.text.Normalizer - code using this may break in time.
It is used internally by the Collator class
package sun.text;
public class Normalizer {
public static Mode COMPOSE;
public static Mode COMPOSE_COMPAT;
public static Mode DECOMP;
public static Mode DECOMP_COMPAT;
public static String normalize(String str, Mode mode, int options);
public static String compose(String source, boolean compat, int options);
public static String decompose(String source, boolean compat, int options);
}
Collator class is the major public one for testing
strings
boolean equals(String source,
String target) and a string comparison method
int compare(String source, String target)
-
Collator can take a Locale
parameter in the contructor or use the default locale
-
Collator is an abstract class that must be subclassed.
The JDK supplies one subclass RuleBasedCollator
Collator applies the normalization rules of
compose/decompose/compatable/non-compatable of
Normalizer
setDecomposition(int decompositionMode)
CANONICAL_DECOMPOSITION (Normalization Form D)
FULL_DECOMPOSITION (Normalization Form KD)
NO_DECOMPOSITION (default)
| Strength | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| PRIMARY | The base letters are different | A versus B |
| SECONDARY | The base letters are the same, but the accents are different | A versus Á |
| TERTIARY | The letters are the same but differ by case | A versus a |
| IDENTICAL | The letters are identical | A versus A |
Collator class has a factory method that takes a Locale
Collator.getInstance(Locale)Collator orders string according to the locale rules
and collator strength and canonicalisation
if (collate.compare(str1, str2) > 0) ...
You can make your own rules for RuleBasedCollator
Collections has a static method
sort(List list, Comparator c)
and Collator implements Comparator
BreakIterator class can be used to segment text
BreakIterator.getCharacterInstance(Locale l);
BreakIterator.getWordInstance(Locale l);
BreakIterator.getLneInstance(Locale l);
BreakIterator.getSentenceInstance(Locale l);
iterator.setText(String s)
int iterator.first();
int iterator.next();
int iterator.DONE
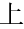
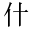
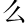 consisting of a one-character word and a two-character word.
consisting of a one-character word and a two-character word.